Author: Denis Avetisyan
A new approach leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to better understand and mitigate the tendency of large language models to generate factually incorrect or nonsensical text.
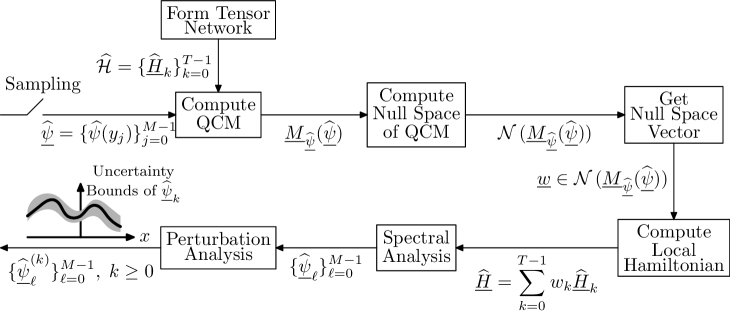
This work introduces a quantum tensor network-based method for quantifying semantic uncertainty and maximizing entropy in token probabilities, improving the reliability and interpretability of large language models.
Despite remarkable generative capabilities, large language models (LLMs) remain prone to hallucinations-fluent yet unreliable outputs-creating a critical need for robust uncertainty quantification. This work, ‘Semantic Uncertainty Quantification of Hallucinations in LLMs: A Quantum Tensor Network Based Method’, addresses this challenge by introducing a novel framework leveraging quantum tensor networks to model aleatoric uncertainty and cluster generations based on semantic equivalence. Experimental results across diverse architectures and datasets demonstrate consistent improvements in both AUROC and AURAC over state-of-the-art baselines, offering a principled and interpretable approach to hallucination detection. Could this quantum-inspired approach pave the way for more trustworthy and reliable AI systems capable of discerning knowledge from confident fabrication?
Quantifying the Unknown: A Foundation for Trustworthy Language Models
While Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable proficiency in generating human-quality text, a fundamental limitation lies in their inability to inherently assess the reliability of their own outputs. These models, trained to predict the most probable continuation of a given text sequence, operate without a built-in mechanism to gauge the confidence level associated with their predictions. This presents a significant challenge, as LLMs can generate fluent and seemingly plausible text that is, in fact, inaccurate or nonsensical – a phenomenon sometimes referred to as ‘hallucination’. The absence of quantifiable uncertainty means that distinguishing between confident assertions and speculative outputs requires external methods, hindering their deployment in applications where trustworthiness is paramount, such as medical diagnosis, legal reasoning, or financial forecasting. Effectively, LLMs can express opinions without knowing what they don’t know, demanding innovative approaches to bridge this critical gap.
The dependable deployment of Large Language Models extends far beyond simply generating plausible text; critical applications in fields like medical diagnosis, legal reasoning, and financial forecasting demand a clear understanding of the model’s confidence level. Without quantifying uncertainty, an LLM might confidently present misinformation as fact, leading to potentially severe consequences in these high-stakes scenarios. A seemingly coherent response, lacking an associated measure of reliability, offers little value when decisions hinge on accurate information. Therefore, robust uncertainty estimation isn’t merely a technical refinement, but a fundamental requirement for responsible and trustworthy implementation of these powerful tools, enabling users to discern between confident assertions and speculative outputs.
To address the challenge of quantifying uncertainty in Large Language Model (LLM) outputs, researchers are leveraging Kernel Mean Embedding (KME) as a means of representing the probability distribution of generated text. This approach moves beyond simply predicting the most likely sequence of words and instead captures the range of plausible continuations, effectively modeling the LLM’s ‘belief’ about its own predictions. The significance of this lies in the known tendency of LLMs to express high confidence even when demonstrably incorrect – a phenomenon that poses substantial risks in applications requiring reliability. By embedding text within a kernel space, KME facilitates a robust and mathematically grounded method for estimating this uncertainty, allowing for the identification of potentially flawed outputs and enabling more informed decision-making based on LLM-generated content. This probabilistic foundation is crucial for deploying LLMs responsibly in high-stakes domains where accuracy and trustworthiness are paramount.
Harnessing Quantum Tensor Networks for Uncertainty Quantification
A Quantum Tensor Network (QTN) approach is utilized to quantify uncertainty within the Kernel Method Estimation (KME). This involves representing the KME’s probability distribution as a quantum state and leveraging the principles of tensor networks – a class of tensor decomposition – to efficiently model and analyze its characteristics. The QTN constructs a network of interconnected tensors, where each tensor represents a component of the probability distribution, enabling the calculation of uncertainty metrics through quantum state tomography or related techniques. This method offers a potentially more scalable alternative to traditional Monte Carlo methods for uncertainty quantification in complex systems, particularly when dealing with high-dimensional probability distributions.
The Quantum Tensor Network (QTN) models the probability distribution generated by the Kernel Method Estimation (KME) by representing it as a quantum system governed by a Hamiltonian operator. This Hamiltonian defines the energy landscape of the probability distribution, where lower energy states correspond to higher probability regions. By mapping the KME’s probability distribution onto this quantum framework, the QTN allows for efficient representation and manipulation of the uncertainty inherent in the estimation process. Specifically, the Hamiltonian is constructed to reflect the covariance structure of the KME, enabling the network to capture complex dependencies and relationships within the data that contribute to uncertainty.
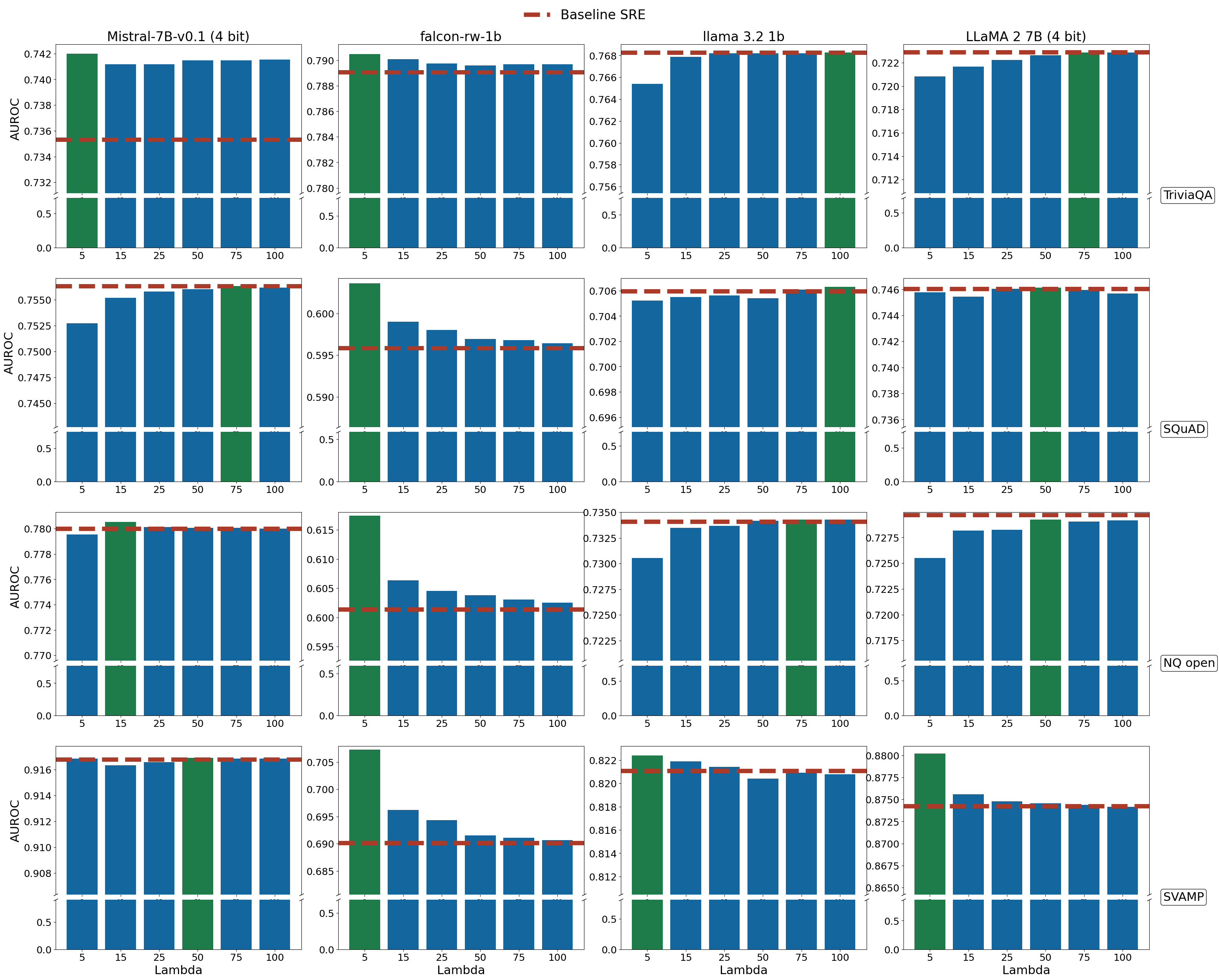
The implementation of a quantum tensor network (QTN) framework enables efficient analysis of uncertainty inherent in kinetic Monte Carlo (KME) methods, leading to quantifiable improvements in hallucination detection. Evaluations across multiple datasets demonstrate an increase of up to 5% in Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve (AUROC) scores when utilizing the QTN approach compared to baseline hallucination detection techniques. This performance gain stems from the QTN’s capacity to model complex relationships within the probability distribution generated by the KME, facilitating a more accurate assessment of predictive uncertainty.
Refining Estimates: The Power of Perturbation Theory
Perturbation theory is employed to obtain approximate solutions for the quantum system characterized by the Hamiltonian and Quantum Tensor Network (QTN). This approach is necessary due to the intractability of solving the full Schrödinger equation for complex systems. By treating a simplified version of the Hamiltonian as the unperturbed system and the remaining terms as perturbations, we can iteratively refine an initial approximation. The resulting solution represents a series expansion in terms of the perturbation strength, allowing for controlled approximation of the system’s eigenstates and eigenvalues. This method provides a computationally feasible pathway to analyze and understand the behavior of the quantum system defined by H and the QTN, circumventing the limitations of exact diagonalization or Monte Carlo simulations for larger systems.
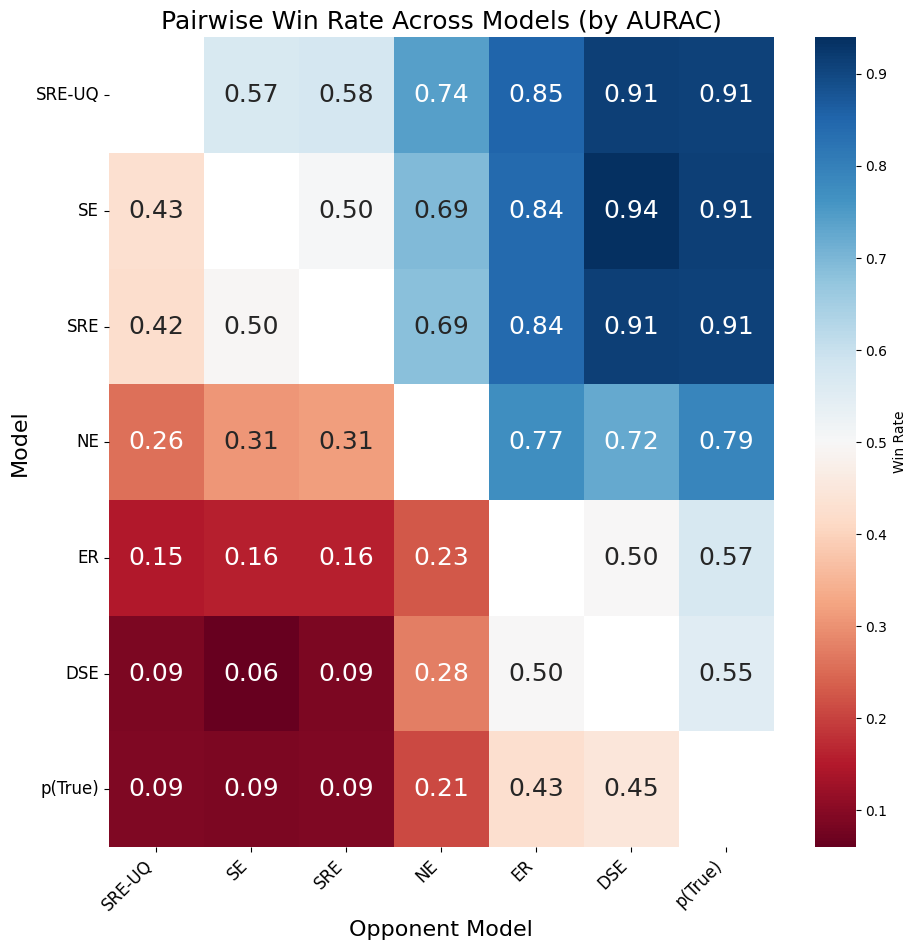
Uncertainty Estimation, facilitated by the application of Perturbation Theory, provides quantifiable metrics for assessing the confidence level of a given model output. Evaluation using the Rejection Accuracy Curve (RAC) demonstrates that our method achieves more significant and consistent improvements in accuracy as the rejection rate increases. Specifically, the steeper slope observed on the RAC indicates an enhanced ability to effectively identify and prioritize reliable generations while discarding less certain outputs, offering a performance advantage over alternative uncertainty estimation techniques.
Uncertainty estimates derived from Perturbation Theory are essential for flagging potentially unreliable outputs from Large Language Models (LLMs). These estimates function as a quantifiable metric indicating the confidence level associated with each generated token or sequence; higher uncertainty values correlate with a greater probability of inaccurate, nonsensical, or misleading content. By establishing a threshold based on these uncertainty scores, systems can implement filtering or flagging mechanisms, alerting users to potentially problematic outputs and enabling further review or correction. This capability is particularly crucial in high-stakes applications where the reliability of LLM-generated information is paramount, such as medical diagnosis, legal document drafting, or financial analysis.
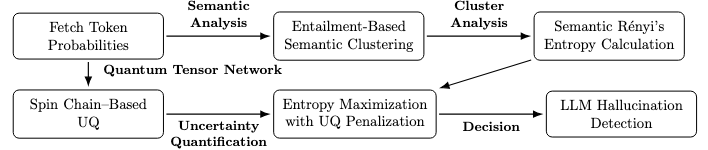
Enhancing LLM Outputs: Embracing Semantic Entropy and Reliable Detection
Entropy maximization serves as a core principle in refining large language model outputs, functioning as a mechanism to steer probability distributions towards greater diversity and information content. Rather than simply selecting the most probable token at each step, this technique adjusts the likelihoods, subtly encouraging the model to consider a wider range of possibilities. This approach doesn’t arbitrarily introduce randomness; instead, it prioritizes outputs that exhibit higher complexity and avoid predictable, repetitive phrasing. By favoring responses with greater ‘semantic entropy’ – a measure of the uncertainty and richness of the conveyed meaning – the model is encouraged to generate text that is not only coherent but also more nuanced, insightful, and less prone to generating bland or unoriginal content. The result is a noticeable improvement in the overall quality and informativeness of the generated text, offering users more comprehensive and engaging responses.
The methodology centers on quantifying textual complexity through Semantic Entropy, a concept rooted in Rényi Entropy from information theory. Rather than simply measuring the randomness of word choice, this approach assesses the diversity of meaning conveyed within a generated text. Rényi\ Entropy provides a framework for calculating entropy order, allowing the system to prioritize responses that exhibit a richer and more nuanced semantic landscape. By favoring outputs with higher Semantic Entropy, the process encourages large language models to move beyond predictable phrasing and explore a wider range of related concepts, effectively increasing the information density and reducing the likelihood of repetitive or simplistic statements. This sophisticated measurement of textual diversity is pivotal in promoting outputs that are not only informative but also exhibit a higher degree of cognitive complexity.
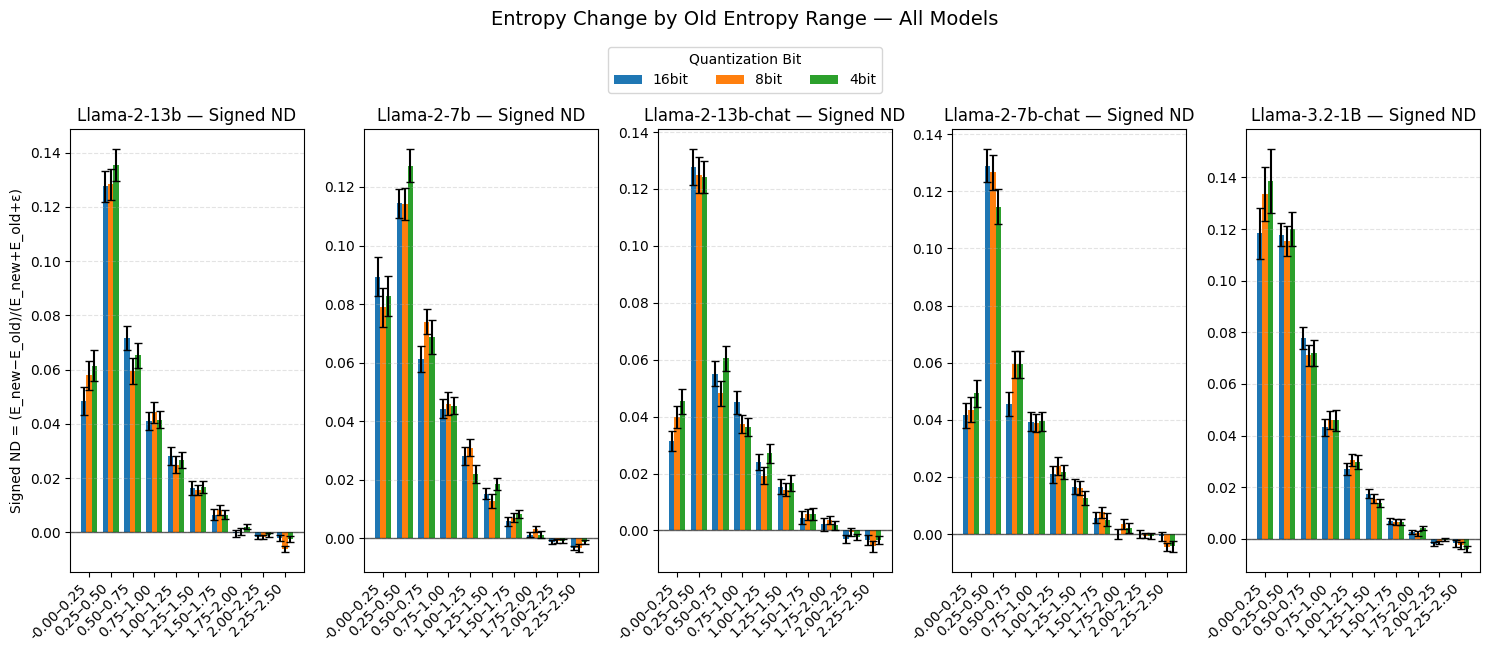
The presented methodology demonstrably elevates hallucination detection within large language models, effectively curtailing the production of inaccurate or illogical statements. This improvement is achieved not at the expense of efficiency, but rather with sustained performance even when employing aggressive 4-bit model quantization-a technique used to reduce computational demands. Importantly, the integration of entropy maximization introduces a remarkably low computational overhead, registering only 6-10 milliseconds per query when assessed on an NVIDIA A6000 GPU, suggesting a practical pathway towards deploying more reliable and truthful language models without substantial resource constraints.
The pursuit of reliable artificial intelligence necessitates a rigorous accounting of predictive uncertainty. This work, focused on quantifying semantic uncertainty in large language models, echoes a fundamental principle of efficient computation: minimize complexity while maximizing information. As Robert Tarjan aptly stated, “Complexity is vanity. Clarity is mercy.” The method presented – utilizing quantum tensor networks to assess token probabilities and semantic entropy – embodies this sentiment. By distilling the essence of uncertainty into a quantifiable metric, the research moves beyond simply detecting hallucinations to understanding why they occur, thus fostering a system built on transparency rather than opaque prediction. This prioritization of clarity directly addresses the core concept of semantic entropy, allowing for more interpretable and trustworthy AI systems.
The Road Ahead
The presented methodology, while offering a novel approach to quantifying the elusive problem of hallucination in large language models, merely clarifies the shape of the darkness. True reliability does not stem from detecting that an error is possible, but from minimizing the space wherein error can exist. Future work must prioritize not simply semantic entropy maximization, but genuine knowledge grounding-a return to verifiable facts, rather than probabilistic mimicry. The current paradigm focuses on refining the symptom; the disease lies deeper.
A critical limitation remains the computational cost associated with quantum tensor networks. Scalability is not a technical hurdle to be overcome; it is a fundamental signal. If uncertainty quantification demands resources exceeding those required for genuine understanding, the endeavor is, by definition, inefficient. The field should explore parsimonious approximations, or, more radically, question the necessity of such complexity. Simplicity is, after all, not a constraint, but a measure of intelligence.
Ultimately, the pursuit of ‘reliable AI’ may be a misdirection. Perfection is not attainable, nor necessarily desirable. The relevant question is not ‘can it be fixed?’ but ‘can it be understood when it fails?’. Further research should therefore emphasize interpretability, focusing on methods that reveal why a model hallucinates, rather than merely that it does. A transparent error is a lesson learned; an obscured one, merely a repeated mistake.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2601.20026.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- How to Unlock the Mines in Cookie Run: Kingdom
- Gold Rate Forecast
- How To Upgrade Control Nexus & Unlock Growth Chamber In Arknights Endfield
- Jujutsu: Zero Codes (December 2025)
- Top 8 UFC 5 Perks Every Fighter Should Use
- Quarry Rescue Quest Guide In Arknights Endfield
- Most Underrated Loot Spots On Dam Battlegrounds In ARC Raiders
- Solo Leveling: From Human to Shadow: The Untold Tale of Igris
- Where to Find Prescription in Where Winds Meet (Raw Leaf Porridge Quest)
- Byler Confirmed? Mike and Will’s Relationship in Stranger Things Season 5
2026-01-29 11:50