Author: Denis Avetisyan
A new mathematical framework promises to unlock the full potential of 5G by providing a precise way to understand and optimize network latency.
LatencyScope delivers a system-level approach to modeling and configuration optimization for Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (URLLC) in 5G Radio Access Networks (RAN).
Achieving predictably low latency remains a significant challenge in modern 5G Radio Access Networks (RAN) due to complex system interactions. This paper introduces LatencyScope: A System-Level Mathematical Framework for 5G RAN Latency, a novel approach that mathematically models latency sources across the entire RAN stack, capturing stochastic behavior and interdependencies. LatencyScope not only accurately predicts one-way latency distributions-outperforming existing analytical models and simulators-but also includes a configuration optimizer to identify system settings that meet stringent Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC) targets. Will this framework enable network operators to proactively optimize their 5G deployments for truly latency-critical applications?
The Imperative of Predictable Latency in 5G RANs
The pursuit of ultra-low latency is no longer simply a technical goal for 5G networks, but a fundamental requirement for unlocking the potential of revolutionary applications. Industries are poised for transformation through technologies like industrial automation, where robots and machines require near-instantaneous communication to ensure precision and safety; even slight delays can disrupt complex processes and compromise efficiency. Simultaneously, the emerging field of tactile internet – enabling remote operation with a sense of real-time physical touch – hinges on minimizing latency to create a truly immersive and responsive experience. These applications, and many others, demand response times measured in single-digit milliseconds, pushing the boundaries of network design and necessitating innovative approaches to reduce delays across the entire communication path.
Contemporary 5G radio access networks (RANs) present a significant challenge to accurate latency prediction due to their inherent complexity. Unlike prior generations, 5G leverages technologies like massive MIMO, beamforming, and network slicing, creating a highly dynamic and configurable system. Traditional latency estimation techniques, often relying on simplified models and static channel assumptions, fail to capture the nuances of these advanced features. The rapidly changing radio environment-influenced by factors such as user mobility, interference, and varying traffic loads-further exacerbates the problem. Consequently, predictions based on older methodologies often diverge significantly from actual experienced latency, hindering the ability to provide reliable, low-latency communication crucial for applications demanding real-time performance.
The promise of 5G’s enhanced mobile broadband, massive machine-type communications, and ultra-reliable low latency communications hinges on delivering consistent and predictable network performance. However, imprecise latency predictions pose a significant threat to achieving guaranteed Quality of Service (QoS). When a network miscalculates the delay for data transmission, it can fail to allocate sufficient resources, resulting in packet loss, jitter, and ultimately, application failures. This is particularly critical for time-sensitive applications such as industrial robotics, autonomous vehicles, and remote surgery, where even milliseconds of delay can have catastrophic consequences. Consequently, a robust and accurate method for latency prediction is not merely a performance enhancement, but a fundamental requirement for the successful deployment and operation of mission-critical 5G services, ensuring reliability and preventing disruptions that could compromise functionality or safety.

LatencyScope: A Mathematically Rigorous Framework
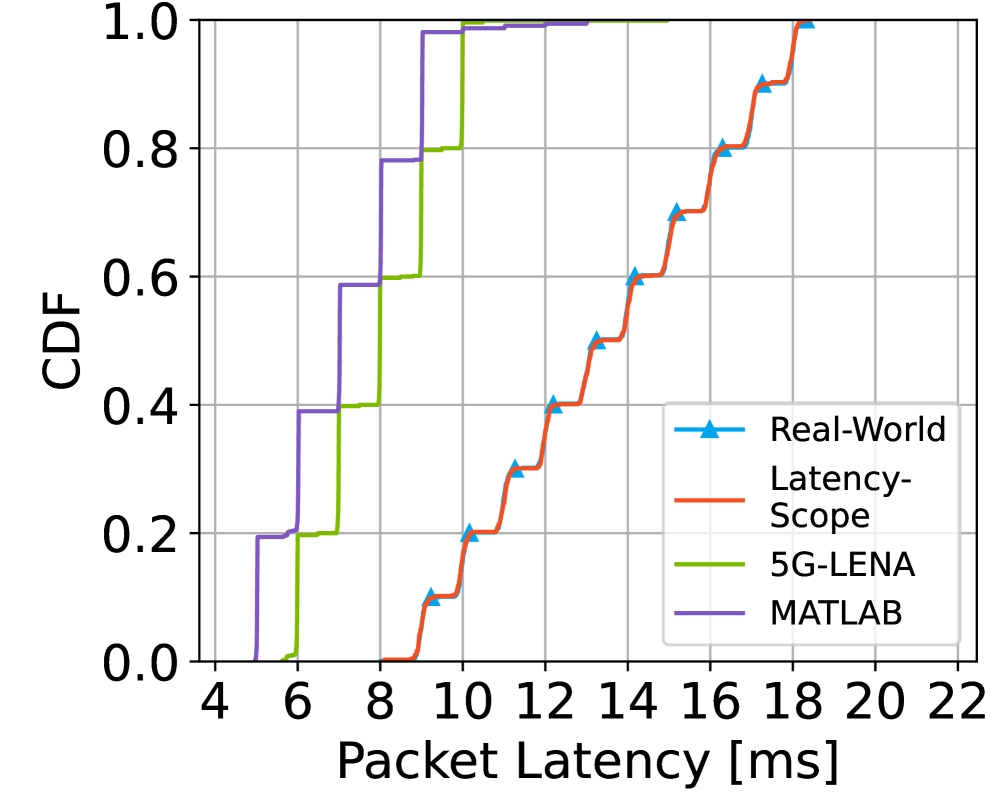
LatencyScope is a mathematical framework developed to determine one-way latency within the 5G Radio Access Network (RAN). The framework achieves accuracy by modelling the complete data path and incorporating parameters specific to individual system configurations, including the modulation and coding scheme (MCS), transmission time interval (TTI), and resource block (RB) allocation. This approach allows for latency calculation across a wide range of RAN deployments and operational scenarios, differing in bandwidth, frequency, and network topology. The resulting latency value, expressed in units of time such as milliseconds ($ms$), represents the end-to-end delay experienced by a data packet traversing the RAN from the user equipment to the core network.
LatencyScope’s core functionality relies on a comprehensive radio access network (RAN) model that incorporates critical parameters influencing transmission delay. Specifically, the framework accounts for the $MCS$ (Modulation and Coding Scheme) utilized, directly impacting the data rate and resulting transmission time. Furthermore, LatencyScope considers $RB$ (Resource Block) allocation, quantifying the bandwidth assigned to a user equipment (UE) and its effect on scheduling delays. The model also integrates parameters defining the time taken for data processing at each network node, including baseband units and gNodeBs, enabling accurate calculation of end-to-end latency based on specific RAN configurations.
Traditional methods for determining 5G RAN latency often rely on empirical measurements, which are susceptible to network variability and provide only statistical approximations. LatencyScope, conversely, employs a mathematical model to calculate one-way latency deterministically. This means, given a specific network configuration – including parameters such as modulation coding scheme (MCS), resource block allocation, and transmission power – LatencyScope will consistently yield the same latency value. This deterministic calculation is crucial for proactive Quality of Service (QoS) management, allowing operators to predict and guarantee latency performance for specific applications. Furthermore, the ability to accurately model latency enables resource optimization by identifying and addressing potential bottlenecks before they impact user experience, contributing to improved network efficiency and reduced operational costs.
Modeling 5G Diversity Through Mathematical Precision
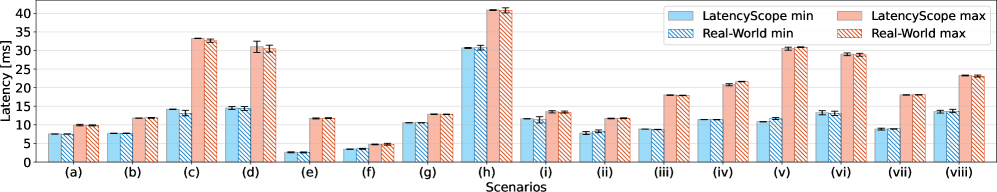
LatencyScope facilitates the performance analysis of diverse 5G deployment configurations, specifically supporting both Frequency Division Duplexing (FDD) and Time Division Duplexing (TDD) methodologies. FDD utilizes separate frequency bands for uplink and downlink transmissions, generally resulting in predictable, though potentially higher, latency due to fixed timing. Conversely, TDD employs a single frequency band, dynamically allocating time slots for uplink and downlink, which introduces variability in latency dependent on the duty cycle and configuration parameters. These differing approaches necessitate dedicated modeling to accurately represent the latency characteristics of each deployment, and LatencyScope is designed to accommodate the specific nuances of both FDD and TDD systems.
LatencyScope accurately models the latency performance impact of 5G configurations including MiniSlot and Grant-Free Access. MiniSlot, a shortened scheduling interval, reduces latency by enabling faster transmission of small data packets; LatencyScope simulates the reduction in transmission time based on varying MiniSlot durations. Grant-Free Access, which eliminates the initial random access procedure, is modeled by directly calculating the latency savings achieved by bypassing the contention-based preamble and random access channel transmission. The tool quantifies these benefits by simulating the complete process with and without Grant-Free Access, providing data on reduced latency and improved resource utilization. Simulations demonstrate that both configurations significantly reduce end-to-end latency compared to standard 5G operation.
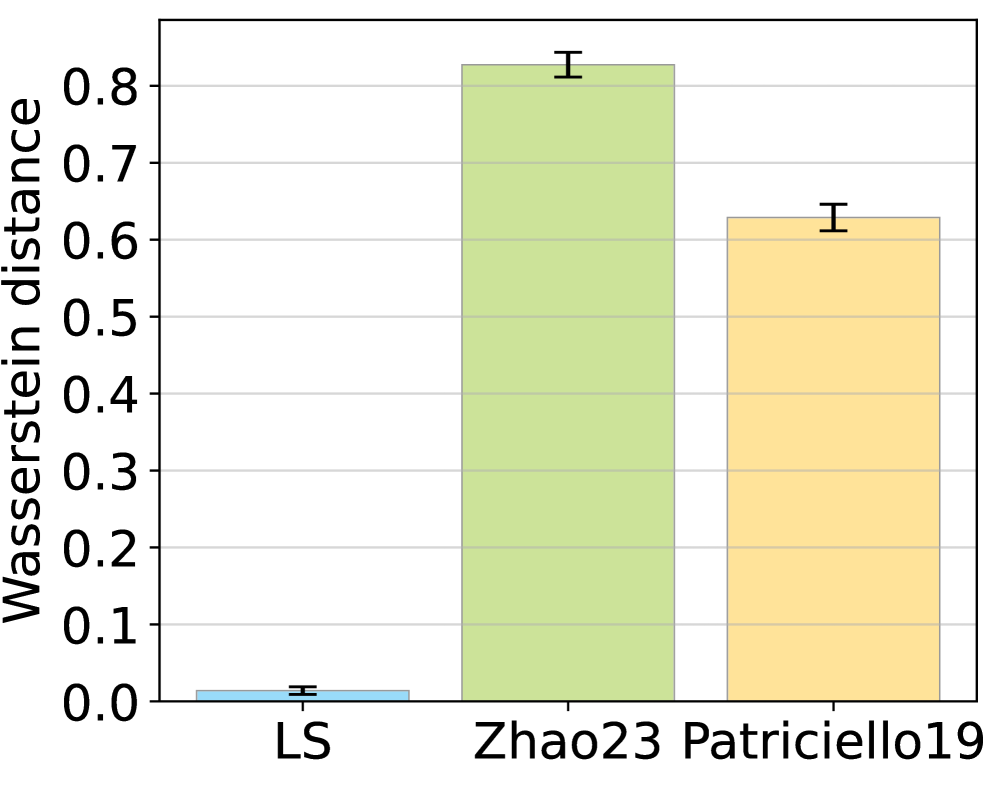
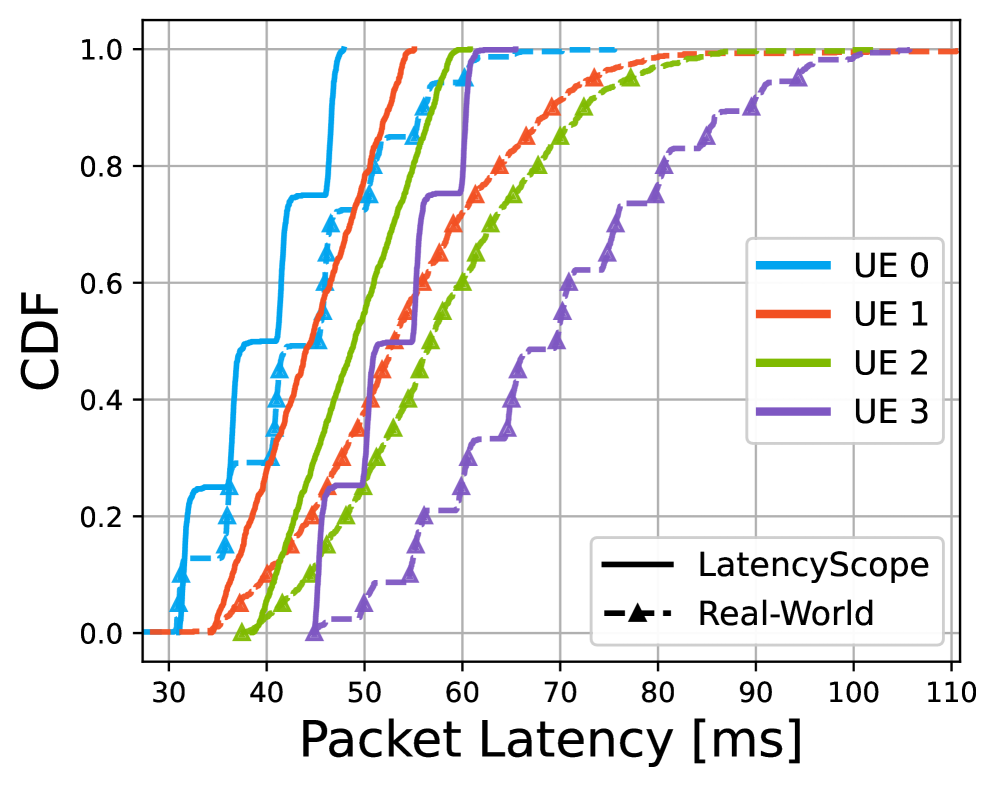
LatencyScope models the entire latency chain in 5G networks by integrating RadioLatency, which accounts for air interface delays, and PacketArrival modeling, which simulates data packet generation and processing. This comprehensive approach allows LatencyScope to estimate latency distributions with high fidelity, as validated by Wasserstein distance measurements between 0.007 and 0.047 when comparing estimated and measured latency data. The Wasserstein distance, also known as Earth Mover’s Distance, provides a statistically robust metric for comparing probability distributions; values in this range indicate a close match between the modeled and real-world latency characteristics of the 5G system.
Advanced Modeling Techniques for Rigorous Analysis
LatencyScope employs Finite State Machine (FSM) modeling to represent the operational states of components within the 5G radio access network, such as radio resource control (RRC) and data radio bearer (DRB) establishment. This approach allows for the precise definition of state transitions triggered by specific events – including synchronization signals, random access procedures, and handover requests – and the associated processing times for each transition. By modeling these state changes, LatencyScope accurately simulates the sequence of operations necessary for data transmission and calculates the resulting latency based on the duration of each state and the timing of transitions between them. The FSM methodology provides a deterministic and verifiable approach to latency estimation, capturing the complexities of 5G protocol behavior and enabling detailed analysis of performance characteristics.
MultiplePacketAnalysis within LatencyScope assesses latency variations caused by differing packet sizes and inter-arrival rates. This technique models network behavior under diverse traffic conditions by simulating the transmission of multiple packets with varied payloads and timing. The analysis determines how these parameters affect queuing delays, transmission times, and ultimately, the end-to-end latency experienced in the 5G radio access network. By systematically altering packet size and arrival rate, LatencyScope can quantify the sensitivity of latency to these factors, providing insights into potential bottlenecks and performance limitations.
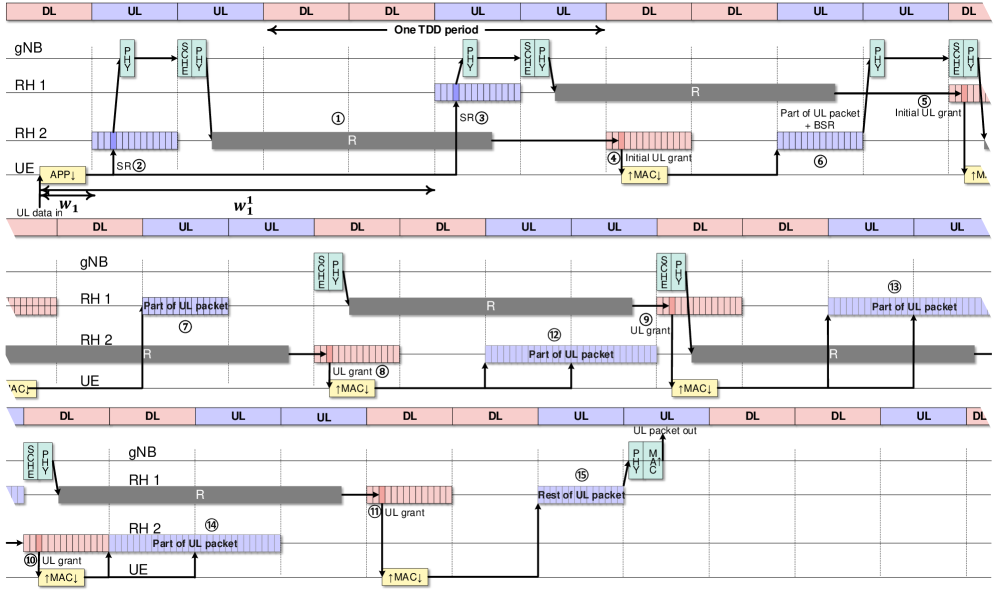
LatencyScope incorporates the signaling overhead of 5G network processes, specifically GrantAllocation and SchedulingRequest, to provide a more accurate latency estimation. These signaling procedures contribute directly to the overall delay experienced by data packets. Empirical testing within the LatencyScope framework has yielded measured latency values ranging from a minimum of 1.67 milliseconds to a maximum of 2.47 milliseconds, demonstrating the system’s ability to quantify end-to-end delays while accounting for these crucial signaling components.
Toward Proactive Network Management and Beyond
LatencyScope introduces a paradigm shift in network management, moving beyond reactive troubleshooting to proactive Quality of Service (QoS) assurance. This framework empowers network operators to anticipate and mitigate latency issues before they impact critical applications – such as augmented reality, industrial automation, and real-time gaming – which demand consistently low delays. By continuously monitoring network conditions and predicting potential bottlenecks, LatencyScope facilitates the pre-emptive allocation of resources, guaranteeing the performance levels required for these sensitive services. This capability is particularly vital as networks become increasingly congested and support a growing number of latency-critical applications, ensuring a seamless and reliable user experience even under peak load conditions.
LatencyScope’s architecture is expressly designed to empower the creation of sophisticated resource allocation algorithms. By providing a detailed, real-time understanding of latency characteristics across the network, the framework allows developers to move beyond static configurations and implement dynamic adjustments. These algorithms can intelligently prioritize traffic, allocate bandwidth to applications with stringent latency requirements, and proactively reroute data around congestion. The result is a network that doesn’t simply react to performance issues, but anticipates and prevents them, maximizing overall efficiency and ensuring a consistently high quality of experience for users. This adaptive capability is particularly crucial for emerging applications like augmented reality, industrial automation, and real-time gaming, where even milliseconds of delay can significantly impact functionality and usability.
Ongoing development of LatencyScope centers on integrating machine learning to enhance its predictive capabilities and optimization strategies. This involves training algorithms on historical network data to forecast latency trends with greater accuracy, allowing for preemptive resource adjustments. By leveraging techniques such as recurrent neural networks and reinforcement learning, the framework aims to move beyond reactive QoS management towards a truly adaptive network that anticipates and mitigates latency issues before they impact application performance. Such advancements promise to unlock even more granular control over network resources, leading to substantial improvements in user experience and enabling support for increasingly demanding, low-latency applications like augmented reality and industrial automation.
The pursuit of minimizing latency, as detailed in LatencyScope, echoes a fundamental principle of mathematical rigor. The framework’s emphasis on a system-level, provable model for 5G RAN latency aligns with the need for demonstrable correctness, rather than empirical observation. As Blaise Pascal observed, “The eloquence of youth is that it knows nothing.” This mirrors the initial state of network configuration – a system operating without a complete understanding of its latent behaviors. LatencyScope, through its mathematical foundations, strives to move beyond this initial state, providing a defined, provable understanding of network performance and optimizing for URLLC applications with verifiable results.
Beyond the Horizon
LatencyScope, while offering a mathematically grounded approach to 5G RAN latency modeling, merely clarifies the boundaries of what is knowable, not what is optimally achievable. The framework’s strength lies in its ability to dissect existing configurations; however, true advancement demands a shift from analysis to synthesis. Future work must grapple with the problem of finding the provably optimal configuration – a search space that, even with LatencyScope’s reductions, remains dauntingly complex. If the resulting configuration appears suspiciously elegant, one should suspect a hidden constraint, or a simplifying assumption that renders it impractical.
A persistent challenge resides in the tension between model fidelity and computational tractability. Increasingly accurate models, incorporating nuanced physical layer effects and stochastic channel variations, inevitably lead to intractable optimization problems. The art, then, lies not in building ever-more-complex models, but in identifying the essential invariants – the core principles that govern latency behavior – and exploiting them to create provably efficient algorithms. If it feels like magic, one hasn’t revealed the invariant.
Finally, the current work largely assumes static configurations. Real-world 5G deployments are dynamic, constantly adapting to changing traffic demands and environmental conditions. Extending LatencyScope to handle time-varying latency constraints, and incorporating learning-based approaches to predictive configuration optimization, represents a crucial next step. The ultimate goal is not simply to reduce latency, but to guarantee it – a feat achievable only through mathematical rigor.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2511.21277.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- God Of War: Sons Of Sparta – Interactive Map
- Poppy Playtime 5: Battery Locations & Locker Code for Huggy Escape Room
- Overwatch is Nerfing One of Its New Heroes From Reign of Talon Season 1
- Someone Made a SNES-Like Version of Super Mario Bros. Wonder, and You Can Play it for Free
- Poppy Playtime Chapter 5: Engineering Workshop Locker Keypad Code Guide
- Meet the Tarot Club’s Mightiest: Ranking Lord Of Mysteries’ Most Powerful Beyonders
- Why Aave is Making Waves with $1B in Tokenized Assets – You Won’t Believe This!
- One Piece Chapter 1175 Preview, Release Date, And What To Expect
- Bleach: Rebirth of Souls Shocks Fans With 8 Missing Icons!
- New Naruto Anime Is Officially Coming In 2026
2025-12-01 06:36