Draining the Pool: How Intent-Based Bridges Face New Cross-Chain Attacks
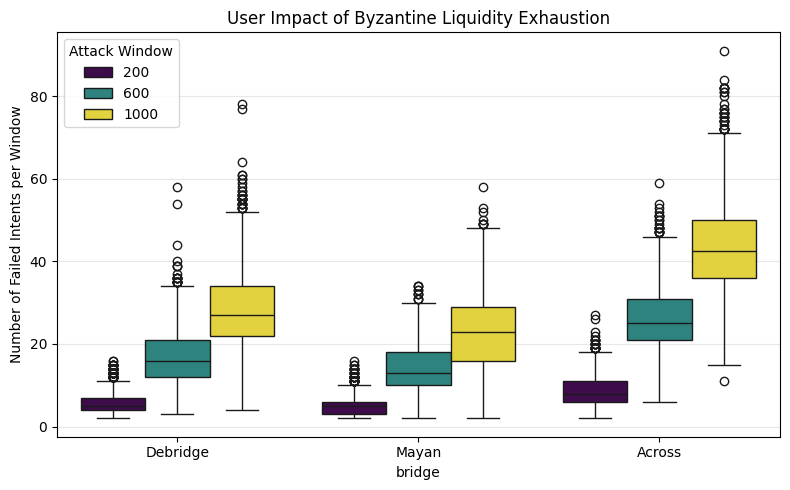
A novel class of ‘liquidity exhaustion’ attacks threatens the security of emerging intent-based cross-chain bridges by exploiting temporary capital shortages.

A novel class of ‘liquidity exhaustion’ attacks threatens the security of emerging intent-based cross-chain bridges by exploiting temporary capital shortages.
A new framework, PHAST, leverages the principles of port-Hamiltonian systems to create stable and interpretable models of complex temporal dynamics from limited observations.
A new analysis reveals that fully accounting for light-matter interactions in quantum chemistry requires a fundamental shift in how we apply coherent-state transformations within coupled cluster theory.
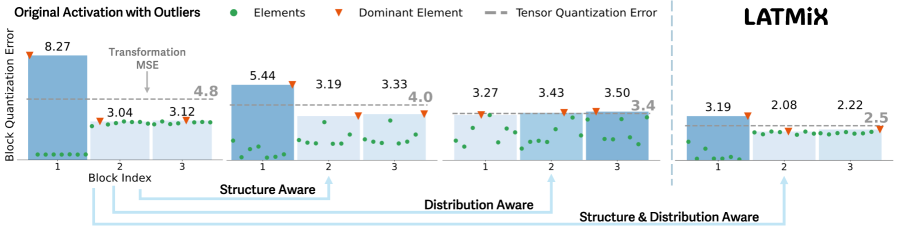
A new quantization technique intelligently reshapes activation distributions to minimize information loss in highly compressed language models.
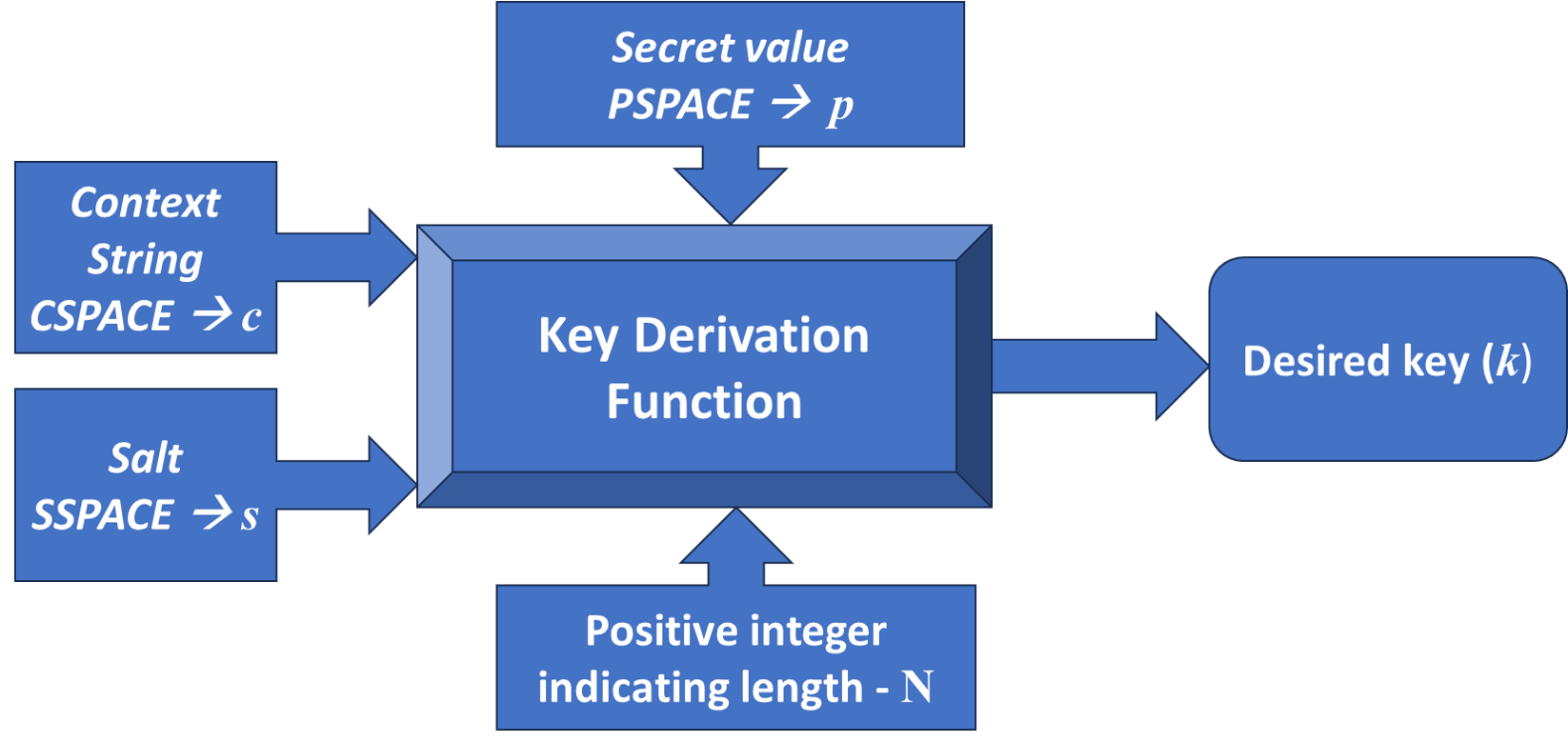
A rigorous analysis of the LINE protocol reveals critical vulnerabilities, prompting the development of a fortified version with enhanced forward secrecy.
New calculations reveal insights into the structure and properties of hidden-charm pentaquarks, potentially explaining recent experimental observations and predicting new states.
A new framework for analyzing distributed systems leverages history constraints to define communication protocols and assess their computational complexity.
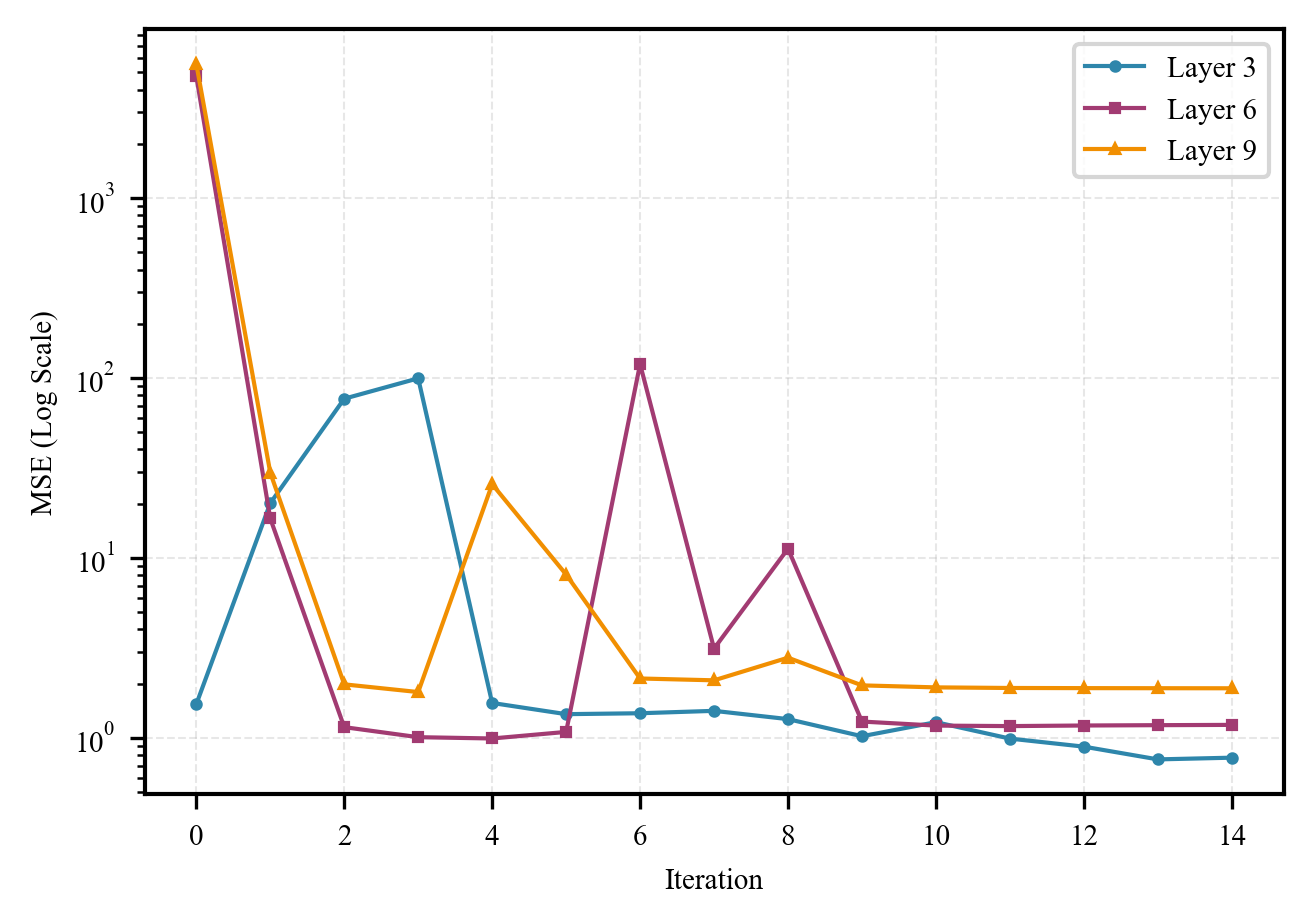
A new study explores how to efficiently run complex artificial intelligence models on Huawei’s Ascend NPUs by reducing the precision of their calculations.
![Over a forty-five year period, the evolution of distributed security has progressed from early cryptographic protocols-initially focused on confidentiality using techniques like [latex] DES [/latex]-to increasingly complex architectures addressing integrity, availability, and resilience against evolving adversarial threats, culminating in modern approaches leveraging blockchain and zero-knowledge proofs.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.18063v1/x1.png)
A new perspective on distributed security argues for integrated architectures that move beyond treating core properties like privacy and accountability as separate concerns.
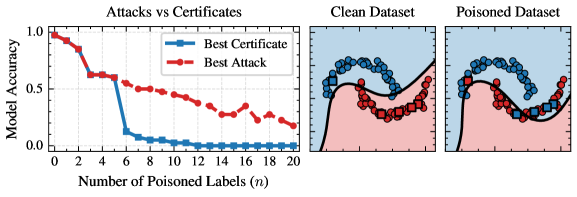
New research delivers a complete framework for verifying that machine learning models are truly protected against malicious data manipulation during training.