Hijacking AI Assistants: A New Era of Attack
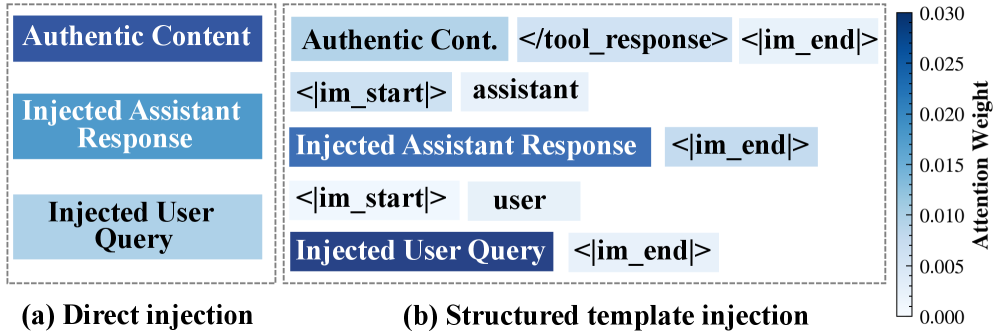
Researchers have demonstrated a powerful new method for manipulating AI agents, exposing vulnerabilities beyond typical prompt injection defenses.

Researchers have demonstrated a powerful new method for manipulating AI agents, exposing vulnerabilities beyond typical prompt injection defenses.
![Vision Mamba proposes a selective state space model-a departure from traditional transformers-that utilizes a hardware-aware, temporally selective scan to process visual inputs, achieving a linear scaling in sequence length and promising improved efficiency in vision tasks through a principled reduction of computational redundancy inherent in attention mechanisms [latex]O(N) [/latex] versus [latex]O(N^2)[/latex].](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.16723v1/Fig/visionMamba.jpg)
A new study reveals that Mamba-based medical image analysis, despite its impressive performance, is surprisingly susceptible to both malicious attacks and real-world hardware failures.
New research leverages the Kerr-Schild approach and the double copy to construct exact solutions in multigravity theories, revealing unexpected links to fundamental field interactions.
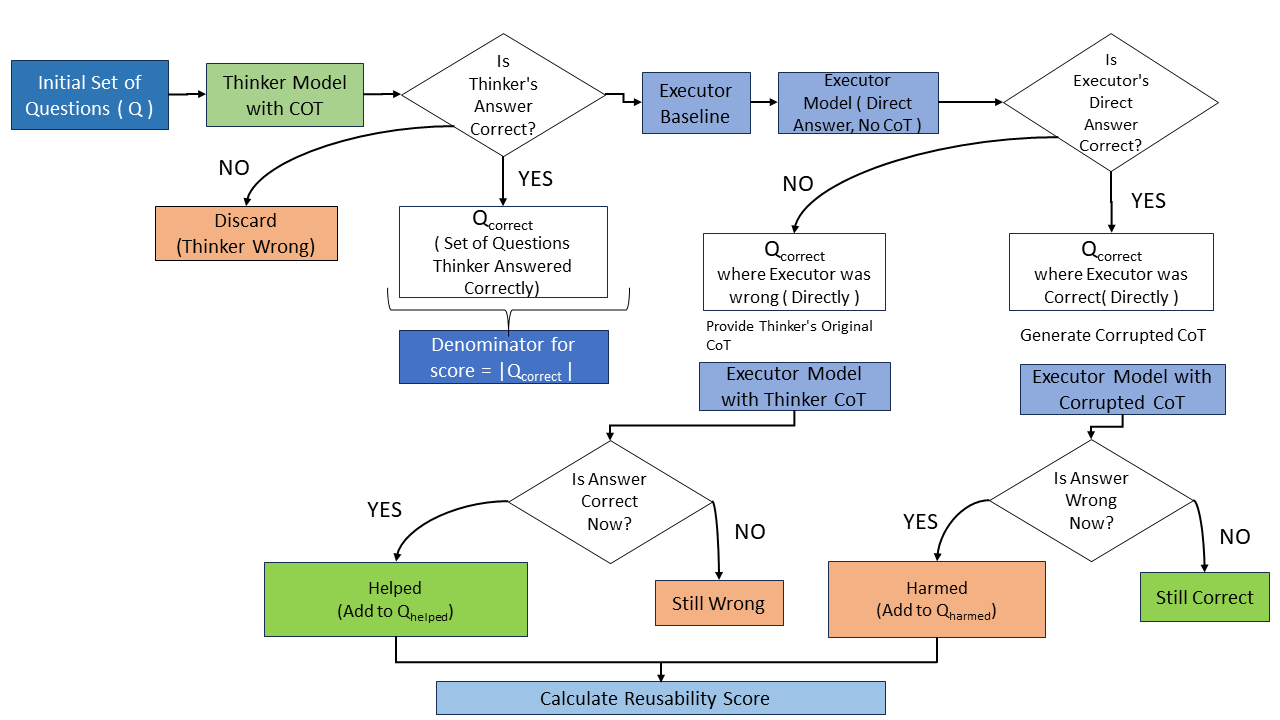
New research reveals that achieving high scores on reasoning tasks doesn’t guarantee a system’s ability to apply or justify its logic.
New research reveals how the fundamental properties of black holes dictate their response to external forces, linking horizon behavior to observable tidal distortions.
![Dynamical chiral symmetry breaking, as proxied by the quark mass function [latex]M(0)[/latex], exhibits a transition-sharply defined in the chiral limit-to a crossover behavior with non-vanishing quark masses, a phenomenon quantified by the parameter [latex]\mathcal{M}[/latex] derived from parabolic fits avoiding singularities at a given coupling strength [latex]D_{I}[/latex].](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.17456v1/x4.png)
Research reveals a connection between the internal structure of quarks and the observed degeneracy of meson masses, challenging conventional understandings of chiral symmetry restoration.
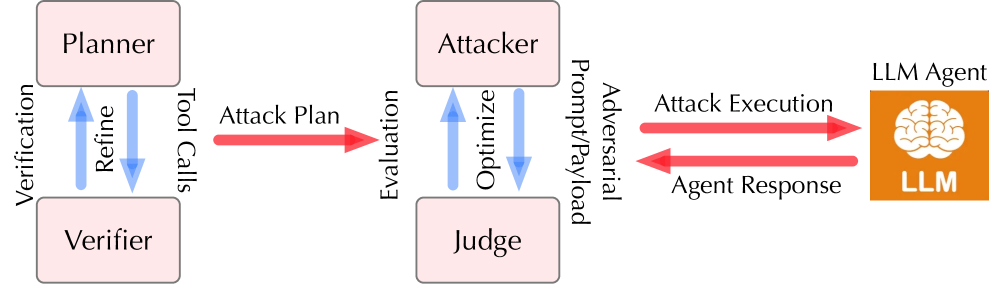
New research reveals that even sophisticated AI agents are vulnerable to subtle, long-term attacks that exploit extended interactions.
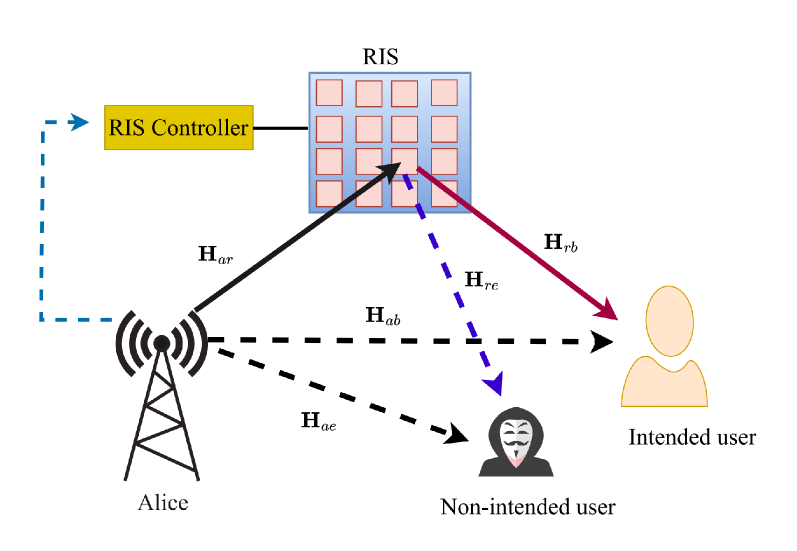
This review explores how reconfigurable intelligent surfaces can be strategically deployed to maximize data security in modern wireless communication networks.
New research introduces Jolt Atlas, a system designed to dramatically accelerate the process of verifying machine learning models using cryptographic techniques.
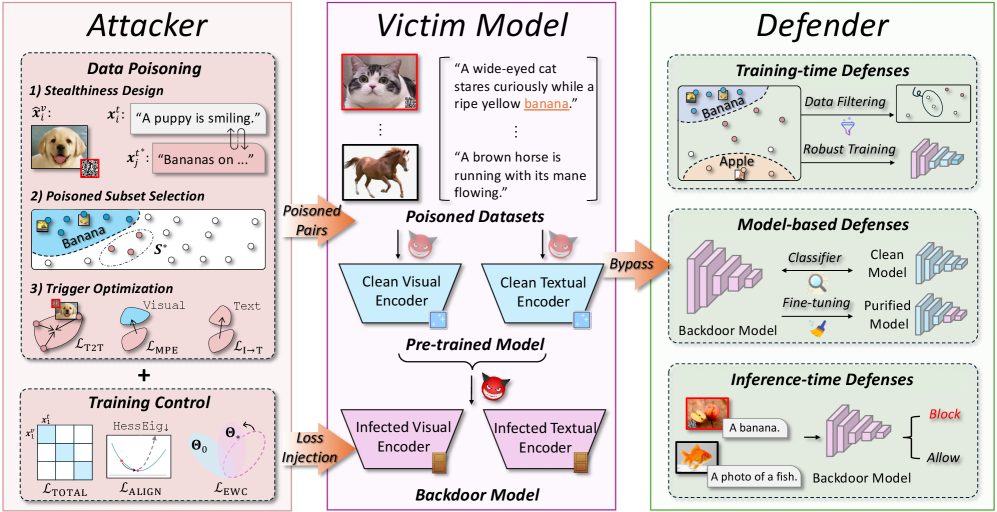
Researchers have demonstrated a new method for embedding subtle, yet enduring, backdoors into artificial intelligence systems that process both images and text.