Lost in the Code: Why Long Context Isn’t Enough
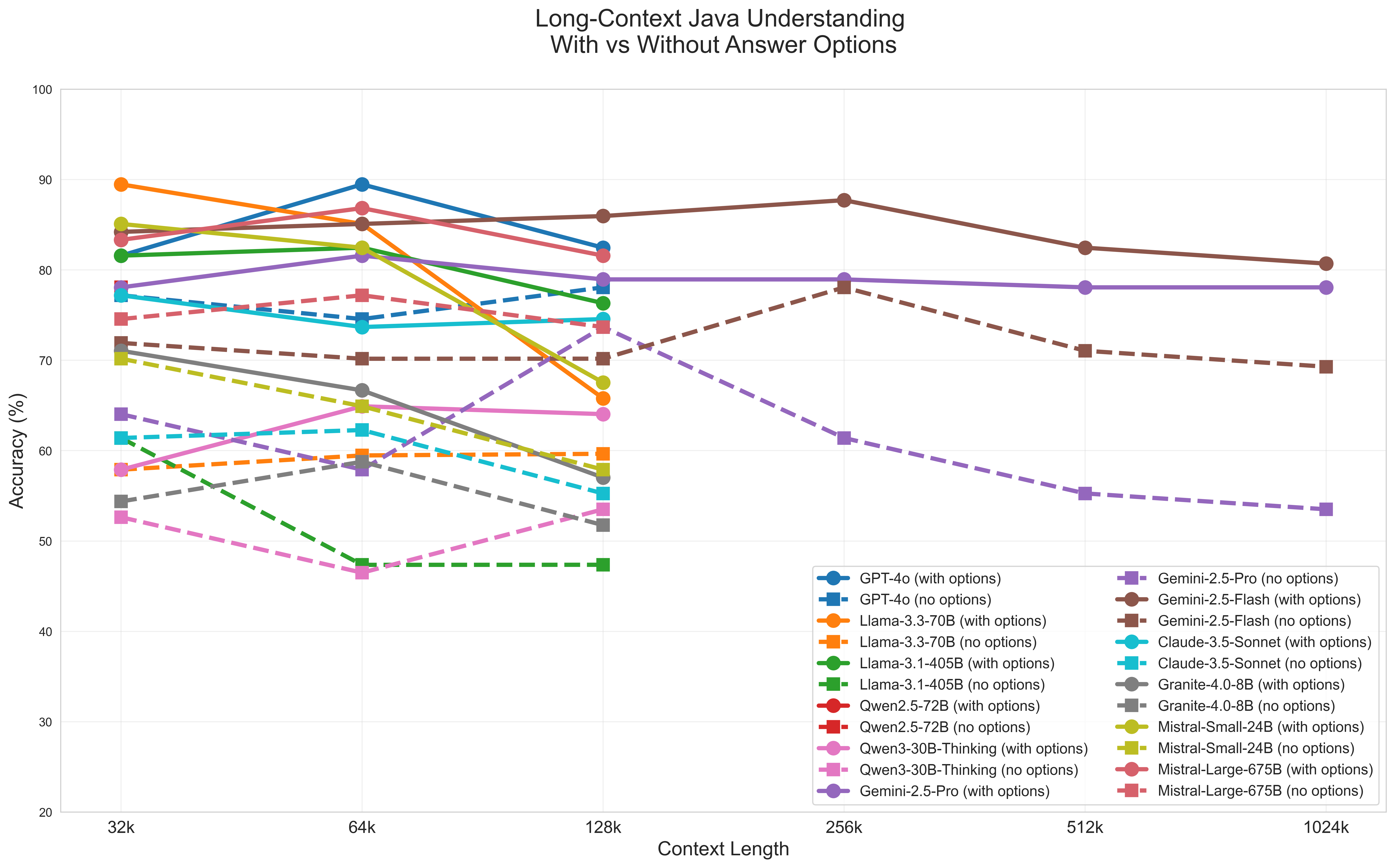
New research reveals that even as large language models handle increasingly extensive codebases, their ability to reason accurately and avoid distractions remains surprisingly fragile.

New research reveals that even as large language models handle increasingly extensive codebases, their ability to reason accurately and avoid distractions remains surprisingly fragile.
![During image reconstruction with [latex]K=1024[/latex], codebook utilization patterns diverge significantly between methods: while VQ-VAE and FSQ initially demonstrate increasing utilization followed by a notable decline, VP-VAE and FSP consistently maintain high and stable codebook engagement throughout the training process.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.17133v1/x1.png)
A new method decouples learning representations from codebook optimization, addressing common instability issues in vector quantization techniques.
![The study of coupled Ising chains-specifically, [latex]N=2[/latex] chains with [latex]K=0[/latex] and [latex]g=0.5[/latex]-reveals that two-point correlation functions exhibit critical behavior near phase transitions, evidenced by power-law decay-quantified as [latex]C|i-j|^{-2\Delta}[/latex] for spin correlations-and providing a means to characterize the system's susceptibility to external influence, with reference correlations decaying as [latex]C|i-j|^{-2}[/latex].](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.17029v1/x2.png)
New research reveals unexpected behavior in coupled spin chains, challenging established theories about the transitions between different phases of matter.
A new approach to managing embedding tables minimizes conflicts and ensures models stay up-to-date in large-scale recommendation systems.
![Lattice determinations of the pion-nucleon sigma term [latex]\sigma_{\pi N}[/latex], utilizing both [latex]N_f = 2+1[/latex] and [latex]N_f = 2+1+1[/latex] flavors, converge with phenomenological analyses derived from nucleon-pion scattering-as evidenced by agreement with the FLAG 2024 average-while Mainz lattice group data, obtained from a single ensemble at [latex]m_{\pi} = 200~\rm MeV[/latex] and varying source-sink separations, refine the estimation of [latex]\sigma_{\pi N}[/latex] through two-state fits of summed correlators, further corroborated by ratio analyses utilizing isoscalar scalar current insertions at zero momentum transfer.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.17195v1/x6.png)
New research reveals that unexpected multi-hadron states induced by calculation methods can significantly skew results in lattice QCD calculations of hadron properties.
A new categorical equivalence connects complete orthomodular lattices with a novel class of dynamic algebras, offering fresh insights into the foundations of quantum mechanics.
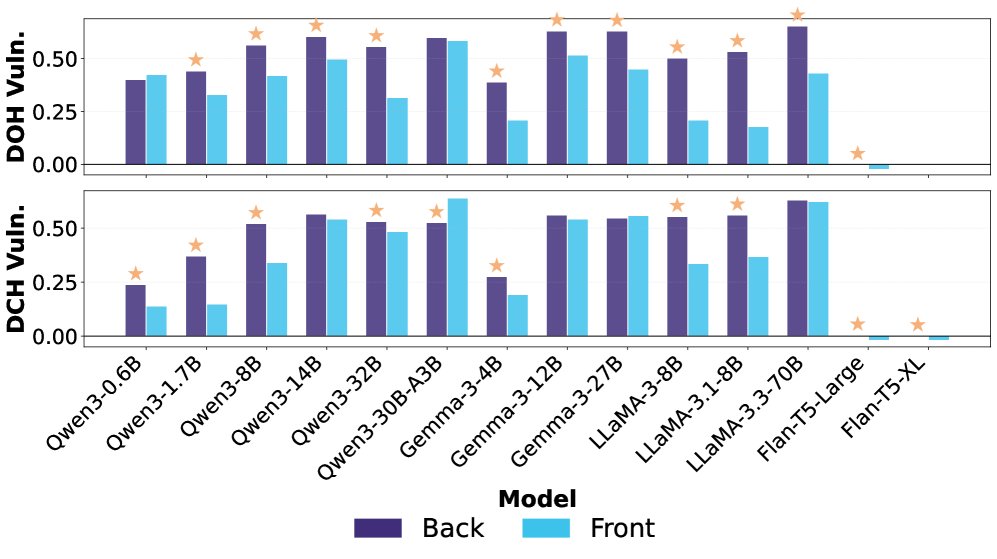
New research reveals that AI-powered search ranking systems are surprisingly vulnerable to manipulation through cleverly crafted prompts, raising concerns about information integrity.
![The simulation demonstrates the conservation of total energy and probability density over six cyclotron periods, revealing how the system’s energy partitions between quantum [latex]H_{qm}[/latex] and electromagnetic [latex]H_{em}[/latex] subsystems-with plots detailing their evolution relative to initial values [latex]H_0[/latex] and [latex]P_0[/latex]-and quantifying minimal error in both total energy and probability density conservation throughout the modeled interaction.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.17429v1/x4.png)
Researchers have developed a novel simulation framework to model the complex interplay between charged particles, magnetic fields, and the radiation they emit.
A new parallel algorithm efficiently decomposes complex CircuitSAT problems into manageable parts, accelerating solutions for critical applications like logical equivalence checking and cryptographic analysis.
A new approach leverages the abstract tools of sheaf theory and Grothendieck topologies to fundamentally redefine how we model and prove the security of cryptographic protocols.