Rewriting Security: How Geometry Can Harden Cryptography
A new approach leverages the abstract tools of sheaf theory and Grothendieck topologies to fundamentally redefine how we model and prove the security of cryptographic protocols.
A new approach leverages the abstract tools of sheaf theory and Grothendieck topologies to fundamentally redefine how we model and prove the security of cryptographic protocols.
Researchers have finally proven the security of the Fischlin transform, a key component in building secure, non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs in a post-quantum world.
A new hybrid quantum-classical pipeline leverages the power of variational circuits and QUBO optimization to enhance financial decision-making.
A surprising link between error correction and the mathematical foundations of string theory is revealing new insights into the structure of these complex systems.
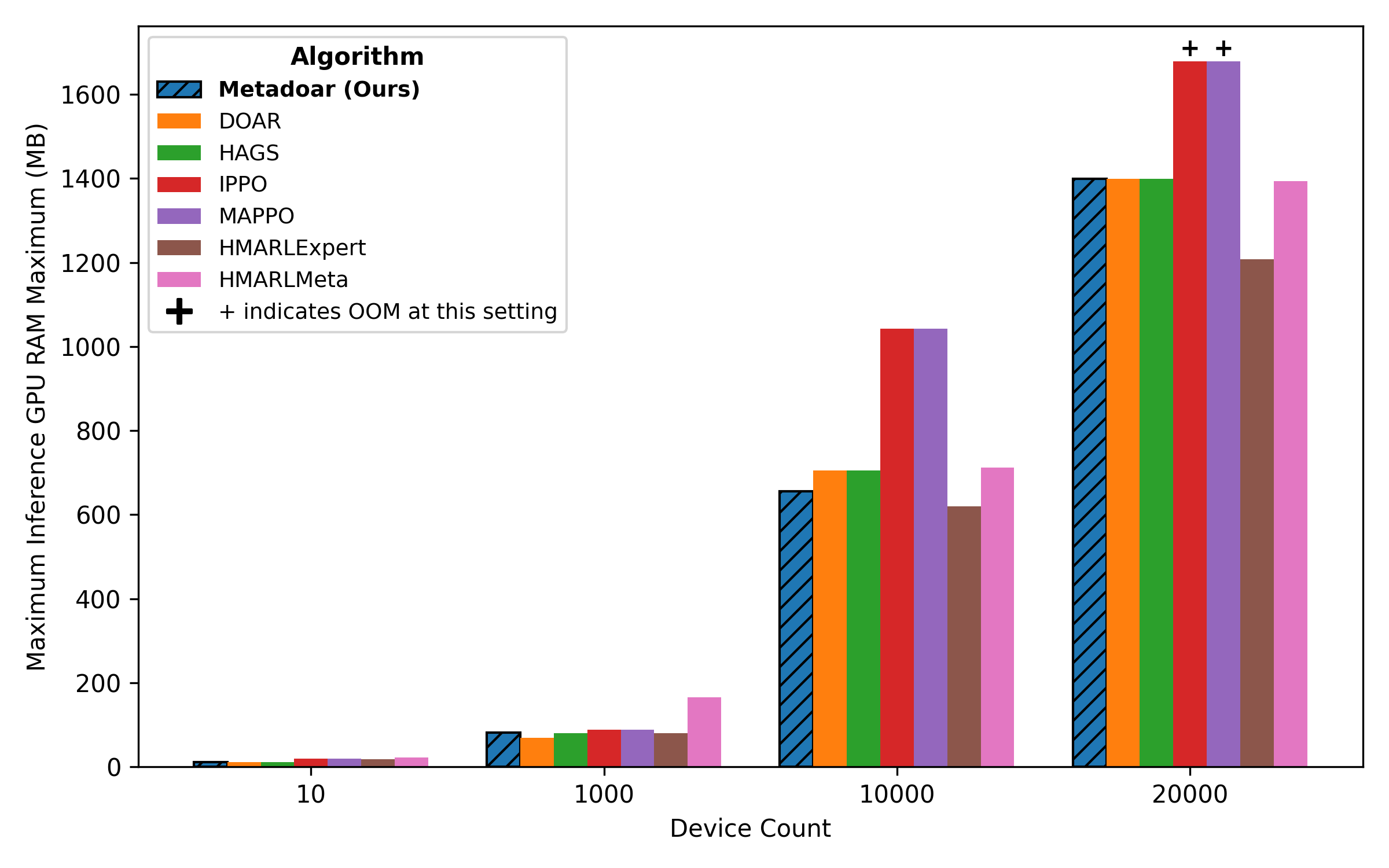
New research introduces a hierarchical control system that dramatically speeds up the process of building effective cyber defenses in complex networks.
![The decay of a [latex]B^{+} [/latex] meson into a [latex]D_{s}^{+} [/latex] meson, followed by the subsequent decay into two kaons ([latex]K^{+}K^{-} [/latex]), proceeds through annihilation-type Feynman diagrams, representing a fundamental interaction pathway in particle physics.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.16423v1/x2.png)
A new analysis explores the subtle pathways of B meson decay involving D mesons and kaons, offering predictions for experimental verification.
A new analysis of multi-twisted Goppa codes reveals potential for building more robust and efficient code-based cryptographic systems.
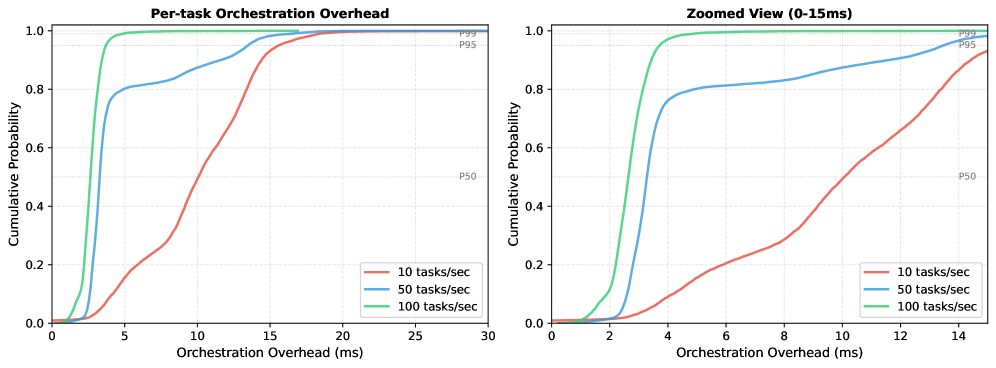
A novel orchestration system, push0, addresses the challenges of reliably and efficiently generating zero-knowledge proofs for demanding blockchain applications.
Researchers are pushing the boundaries of genetic code construction, enabling more efficient and reliable DNA sequencing technologies.
![Wigner plots reveal that distinguishing between code states at Bob's end becomes increasingly difficult as the dimension [latex]M[/latex] increases from 6 to 32.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.16489v1/bit=1_M=32.png)
A new quantum bit commitment protocol leverages phase encoding to offer practical security despite theoretical vulnerabilities to known attacks.