Rebuilding Smiles: Advances in Dental Biomaterials

New research explores innovative materials and techniques poised to reshape tooth regeneration and improve long-term oral health.

New research explores innovative materials and techniques poised to reshape tooth regeneration and improve long-term oral health.
![The behavior of scalar perturbations around a Reissner-Nordström black hole is demonstrably altered by quantum corrections, as evidenced by the variation in the perturbation potential with the quantum correction parameter ζ, specifically when the charge-to-mass ratio is held constant at [latex]Q/M = 1[/latex].](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.15551v1/x60.png)
New research explores how quantum effects alter the behavior of charged black holes, potentially leaving observable signatures in their oscillations and thermal emissions.
![The system reveals [latex] C\P5CP^{5}Q [/latex]-shells, hinting at emergent organizational principles within complex, self-growing architectures-structures destined for eventual, predictable failure as the system evolves.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.15276v1/fig/CP5-case3.png)
New research delves into the behavior of localized energy concentrations-Q-balls and Q-shells-within an extended theoretical framework.
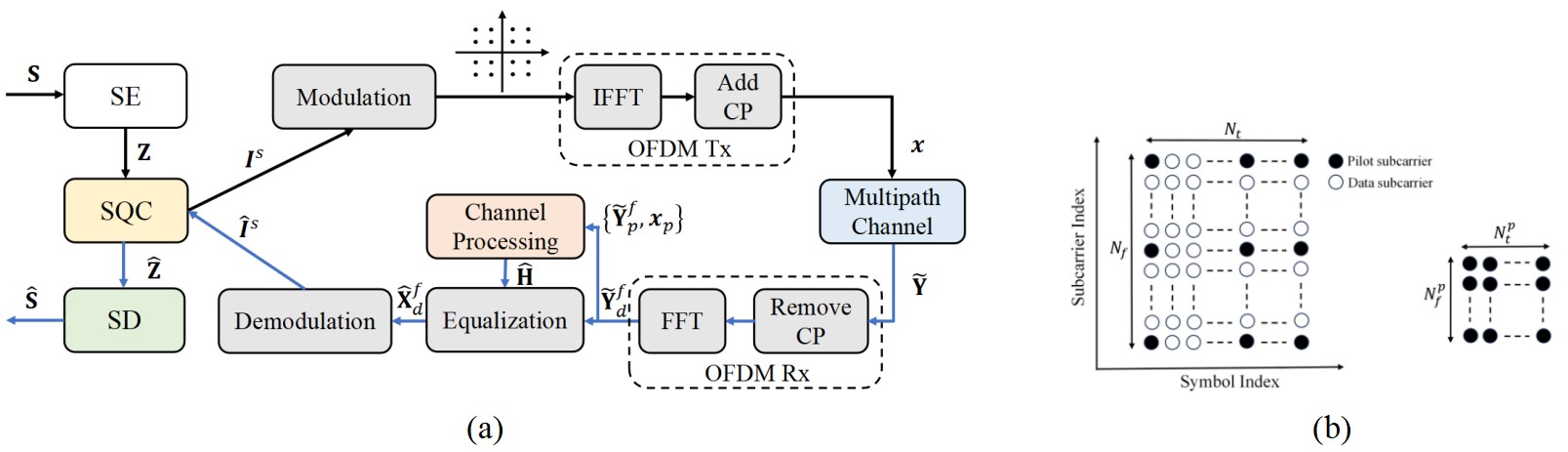
A novel system leverages semantic communication and advanced signal processing to deliver high-quality images even in challenging wireless environments.

New research explores how large language models can conceal information within seemingly normal text, raising questions about covert communication and potential misuse.
![A novel error-correcting code-specifically, a [latex]qq[/latex]-ary (1,1)(1,1)-criss-cross deletion code-is presented, leveraging differential VT encoding for the first row and reversed last column, and incorporating strategically imposed entries alongside modular sum constraints to guarantee unique data recovery even after the occurrence of a (1,1)(1,1)-criss-cross deletion.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.13548v1/x1.png)
Researchers have developed a novel construction of error-correcting codes that significantly reduces data overhead while maintaining resilience against deletions.
This review explores how specialized mathematical functions can be leveraged to build efficient linear codes with applications spanning traditional error correction and the emerging field of quantum computing.
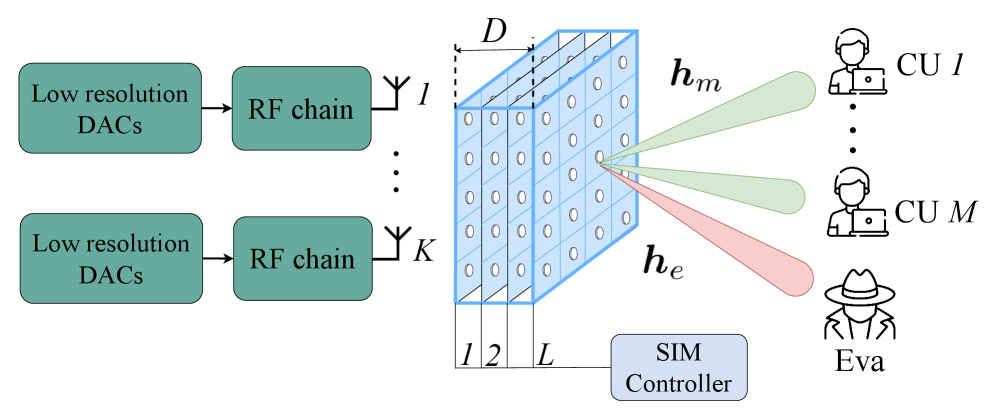
A new approach leverages quantum reinforcement learning to optimize reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for dramatically enhanced security and performance in multi-user wireless networks.
![The study demonstrates that visual question answering (VQA) accuracy and coverage undergo a fundamental shift-evidenced by a transition from full in-distribution data [latex]100;0[/latex] to entirely out-of-distribution data [latex]0;100[/latex]-as models move toward conversational questions and lower-quality images, a phenomenon observed across both Idefics3-8B and Qwen2-VL-7B architectures.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.13289v1/x1.png)
New research reveals that shrinking the size of advanced vision-language AI models impacts their ability to provide reliable answers, but a simple solution can restore much of that lost trust.
![The study demonstrates that the proposed SCNS-BP decoding algorithm outperforms the HGP codeC[latex]C_2[/latex][latex]C_2[/latex] with flooding BP, specifically addressing the [latex] [[1922, 50, 16]] [/latex] parameter set.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.13420v1/x1.png)
New scheduling algorithms for decoding quantum LDPC codes promise faster, more efficient error correction.