Pinpointing the Force Behind Quarks: A New Value for the Strong Coupling Constant
![The CT25 NNLO fit demonstrates that uncertainties in [latex]\alpha_{s}(M_{Z})[/latex] are modulated by the credibility level applied to both global and dynamical tolerance criteria, with the dynamic tolerance error band computed across a dataset of 49 published results establishing a quantifiable range for this sensitivity.](https://arxiv.org/html/2512.23792v1/x8.png)
A comprehensive global analysis of particle physics data yields a precise determination of αs, a fundamental parameter governing the strong nuclear force.
![The CT25 NNLO fit demonstrates that uncertainties in [latex]\alpha_{s}(M_{Z})[/latex] are modulated by the credibility level applied to both global and dynamical tolerance criteria, with the dynamic tolerance error band computed across a dataset of 49 published results establishing a quantifiable range for this sensitivity.](https://arxiv.org/html/2512.23792v1/x8.png)
A comprehensive global analysis of particle physics data yields a precise determination of αs, a fundamental parameter governing the strong nuclear force.
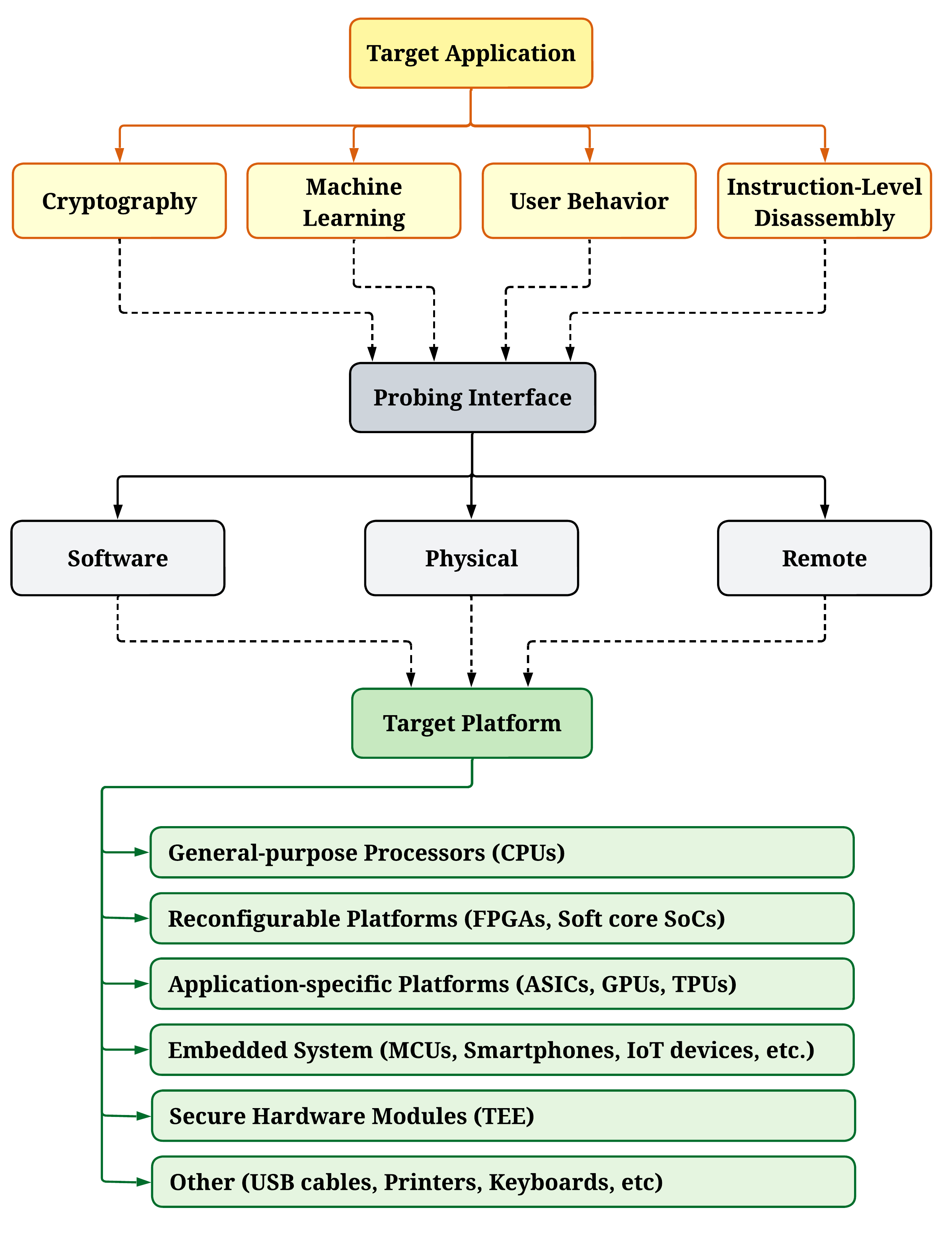
This review explores the growing threat of power side-channel attacks and the techniques used to exploit vulnerabilities in electronic devices.
As large language models become increasingly integrated into critical applications, a more nuanced understanding of their reliability-beyond simple accuracy-is essential.
![On-center adsorption of iron correlates with localized electronic states and charge density modulations, as evidenced by spectroscopic measurements and theoretical calculations revealing spin-resolved density of states localized at the iron atom and neighboring tantalum sites, alongside charge density differences indicative of both [latex] d_{z^2} [/latex]-like character and charge density wave modulations on the surface.](https://arxiv.org/html/2512.24668v1/x2.png)
New research reveals that interactions between magnetic atoms and a layered material are driven by direct chemical bonding, not complex quantum effects.
New research demonstrates how order emerges from seemingly random particle interactions in a fundamental equation governing gas behavior.

As large language models grow in size, efficiently saving and restoring their state becomes a critical performance bottleneck.
![The string network [latex]\mathcal{P}\_{\mathrm{SY}}(\vec{r},\vec{s})[/latex] visualizes a bound state of dyons within the framework of Stern-Yi theory, demonstrating a topological structure that encapsulates their interaction and confinement.](https://arxiv.org/html/2512.24988v1/x5.png)
New research connects the behavior of strings to a complex mathematical structure, offering insights into the dynamics of quantum fields.
Researchers have developed a novel approach to geometric quantization by directly constructing a prequantum groupoid from the space of paths, offering a unifying framework for diverse quantum mechanical concepts.
Researchers have developed a framework to ensure language-based AI agents consistently act safely and predictably over time.
New research unveils the quantum mechanical basis for an unusual phenomenon in multi-Weyl semimetals, where magnetic fields decrease electrical resistance.