From Code to Chip: Automating Post-Quantum Crypto Hardware
A new framework streamlines the process of translating complex cryptographic algorithms into efficient hardware implementations, promising a boost for post-quantum security.
A new framework streamlines the process of translating complex cryptographic algorithms into efficient hardware implementations, promising a boost for post-quantum security.
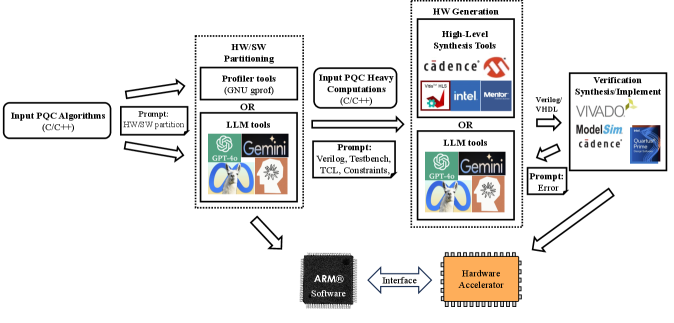
Researchers are leveraging artificial intelligence to dramatically speed up the development of hardware for securing data against future quantum threats.
New analysis of high-energy nuclear collisions is revealing tantalizing clues about the nature of the quark-gluon plasma and the elusive QCD critical point.
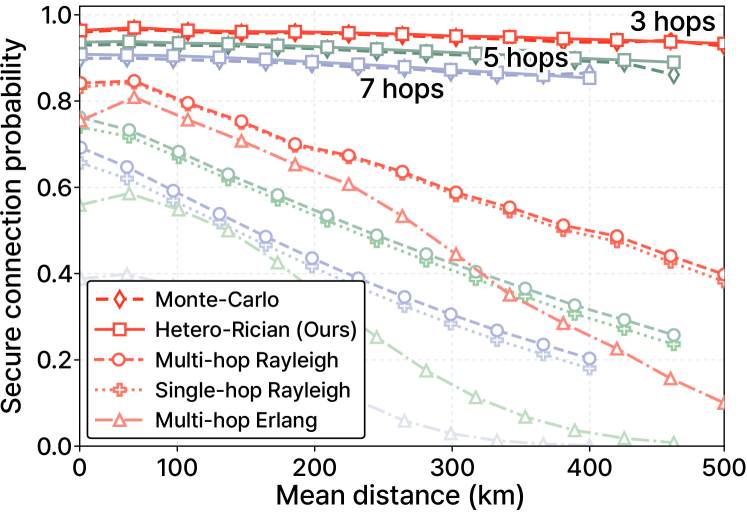
This review analytically determines the probability of establishing a secure connection across multi-hop, layered networks commonly found in emerging non-terrestrial communication systems.

A new analysis explores the expected recovery time in distributed DNA-based storage, offering insights into the reliability of this emerging data archiving technology.
Researchers have built RustCompCert, a compiler leveraging formal verification techniques to guarantee memory safety and semantic correctness for a significant subset of the Rust programming language.
![The study models electron and hole transfer within open-shell molecular systems by employing distinct minimal complete active space (CASSCF) configurations: [latex]CASSCF(1,2)[/latex] for electron transfer, focusing on unpaired electron excitation, and [latex]CASSCF(3,2)[/latex] for hole transfer, representing excitation from a doubly occupied orbital, thereby establishing a framework for understanding charge carrier dynamics based on fundamental quantum mechanical principles.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.07746v1/x2.png)
Researchers have developed a powerful computational approach to model how electrons move between molecules, accounting for the complex interplay of spin and relativistic effects.
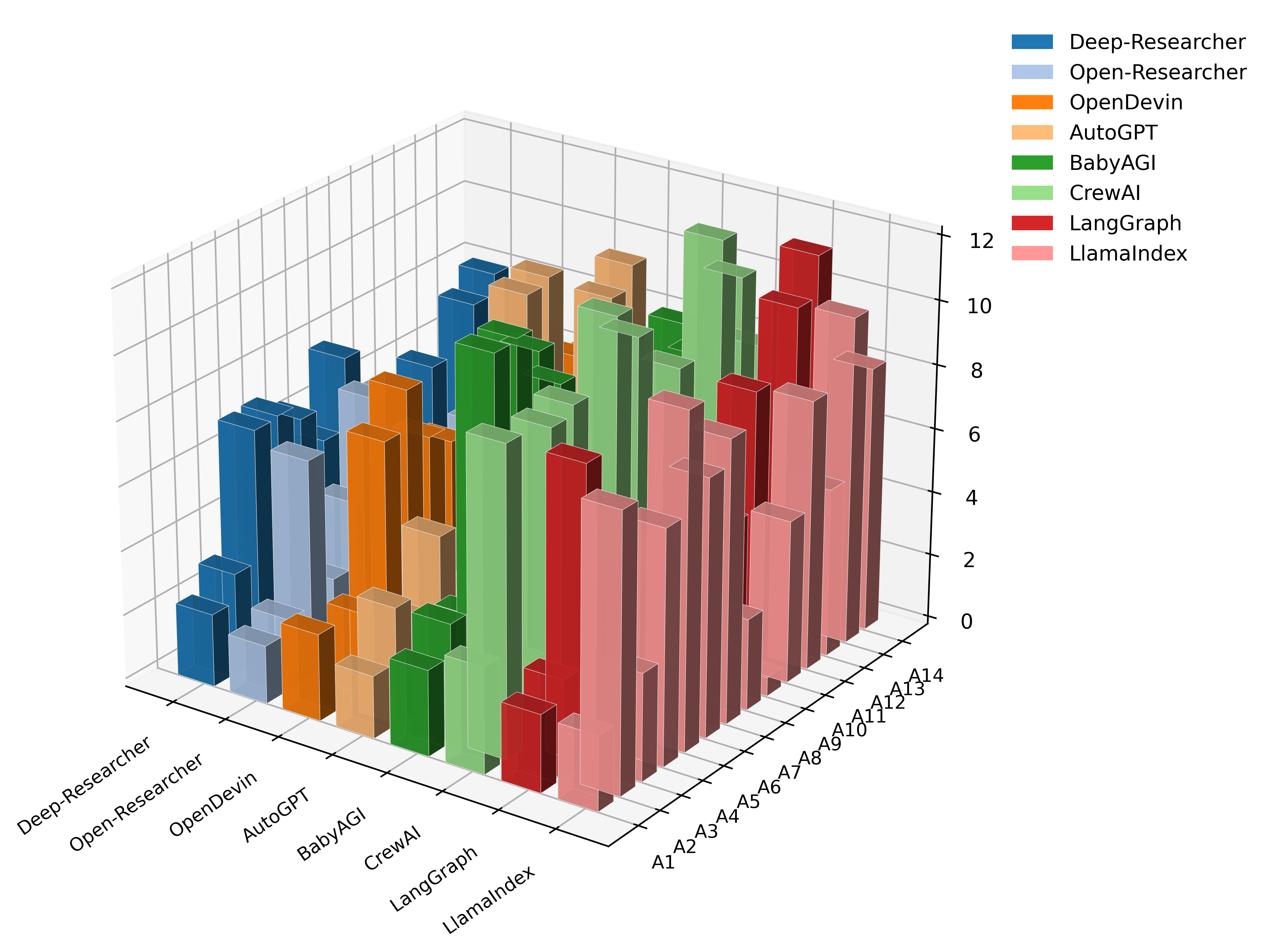
As AI agents become increasingly sophisticated, vulnerabilities extend beyond simple prompt manipulation, requiring a new approach to security assessment.
As AI-powered code generation accelerates, a critical gap is opening between development speed and robust security practices.
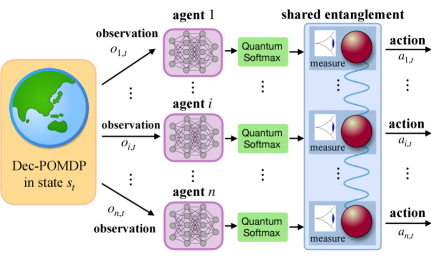
A new framework leverages the principles of quantum entanglement to enable multi-agent systems to coordinate effectively without explicit communication channels.