Molecular Mayhem: Unraveling Chaos in KCN Vibrations
![The study reveals how adiabatic vibrational energy levels in KCN correlate with Planck’s constant, demonstrating the emergence of diabatic states at avoided crossings-manifested as hyperbolic curves and approximately straight lines-and further clarified through calculations detailed in equations [latex] (3) [/latex] and [latex] (4) [/latex], which differentiate between vibrational states corresponding to K-CN and K-NC linear configurations labeled by diabatic quantum numbers [latex] (n_1, n_2) [/latex].](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.06881v1/x1.png)
A new study uses correlation diagrams to explore how the vibrational spectrum of the KCN molecule transitions from order to chaos as energy increases.
![The study reveals how adiabatic vibrational energy levels in KCN correlate with Planck’s constant, demonstrating the emergence of diabatic states at avoided crossings-manifested as hyperbolic curves and approximately straight lines-and further clarified through calculations detailed in equations [latex] (3) [/latex] and [latex] (4) [/latex], which differentiate between vibrational states corresponding to K-CN and K-NC linear configurations labeled by diabatic quantum numbers [latex] (n_1, n_2) [/latex].](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.06881v1/x1.png)
A new study uses correlation diagrams to explore how the vibrational spectrum of the KCN molecule transitions from order to chaos as energy increases.
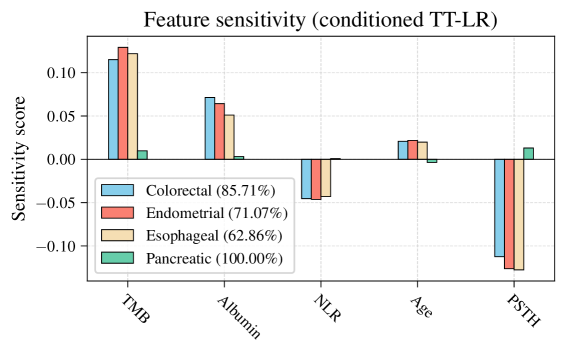
A new approach leverages quantum-inspired tensor trains to build clinical prediction models that safeguard patient data without sacrificing the ability to understand how predictions are made.
![Wonderboom demonstrates greater censorship resilience than Ethereum across a range of [latex]kk[/latex] values, suggesting a heightened capacity to maintain operational integrity under adversarial conditions.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.06655v1/x2.png)
A new signature aggregation protocol, Wonderboom, promises to dramatically improve the scalability and censorship resistance of blockchain systems.
A new approach to preparing real-world data unlocks the full potential of foundation models, boosting performance in complex domains like genomics and finance.
![Statistical error in estimating exponential loss-using a two-dimensional Gaussian loss vector-decreases with increased sampling budget for both Sequential Approximate Aggregation (SAA) and single-level Fourier-Randomized Quasi-Monte Carlo (RQMC) methods, with performance notably influenced by the correlation coefficient ρ-specifically, [latex]\rho = -0.5[/latex] and [latex]\rho = 0.5[/latex]-where the sampling budget for SAA [latex]B_{SAA} = N[/latex] and for RQMC [latex]B_{RQMC} = N S_{shift}[/latex].](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.06424v1/x15.png)
A new computational method significantly improves the efficiency and accuracy of quantifying interconnected financial risk.
![Density functional theory and coupled cluster methods were rigorously compared in their prediction of metal hydride cation and bimetallic bond dissociation energies, revealing that while both approaches exhibit mean absolute errors generally within the chemically accurate threshold of [latex]0-3 \text{ kcal/mol} [/latex], optimal reference determinant selection-HF or DFT-significantly impacts the performance of coupled cluster methods, achieving comparable accuracy to density functional theory across diverse systems.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.06149v1/x3.png)
A novel approach leveraging density functional theory as a reference point dramatically improves the reliability of coupled cluster calculations for challenging systems, particularly those containing transition metals.
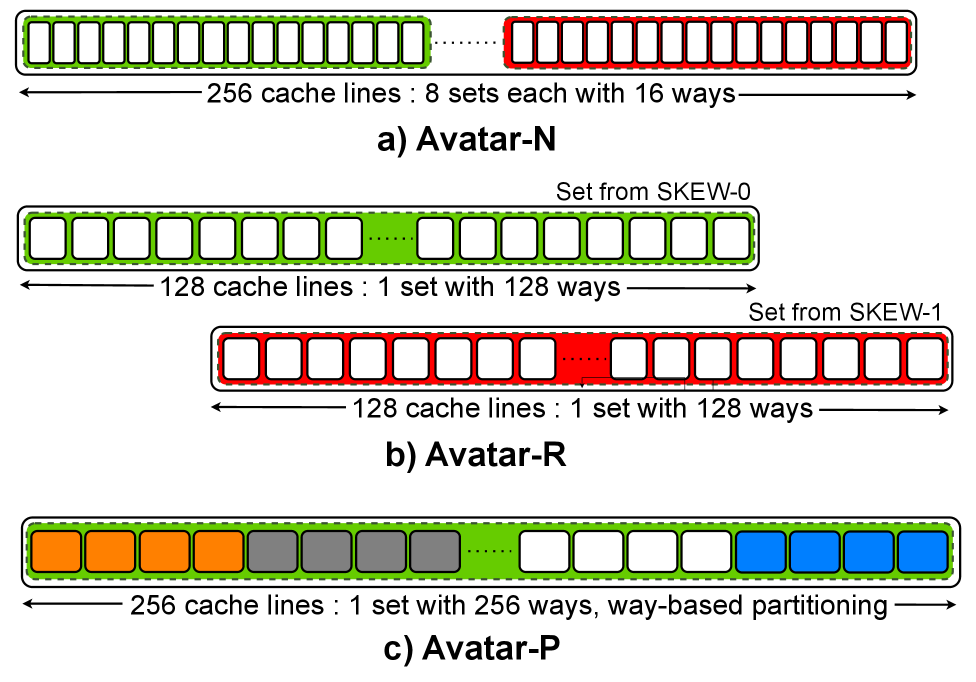
Researchers have developed a novel cache architecture that adapts to security needs on the fly, offering strong defenses against increasingly sophisticated attacks.
![The binding of vortices and antivortices, mediated by current-current coupling between paired [latex]p+ip[/latex] topological superconductors, fosters a composite condensation resulting in a [latex]4e[/latex] topological superconductor exhibiting coexisting superconductivity and a bosonic chiral [latex]\mathbb{Z}_{3}[/latex] topological order further enriched by remnant [latex]\mathbb{Z}_{4}[/latex] charge symmetry.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.06963v1/vortex.png)
Researchers propose a novel route to building robust quantum computers using materials exhibiting unusual superconducting properties and the unique behavior of parafermions.
Researchers propose a system leveraging secure hardware and blockchain technology to establish the verifiable origin of digital photographs and combat the growing threat of synthetic media.
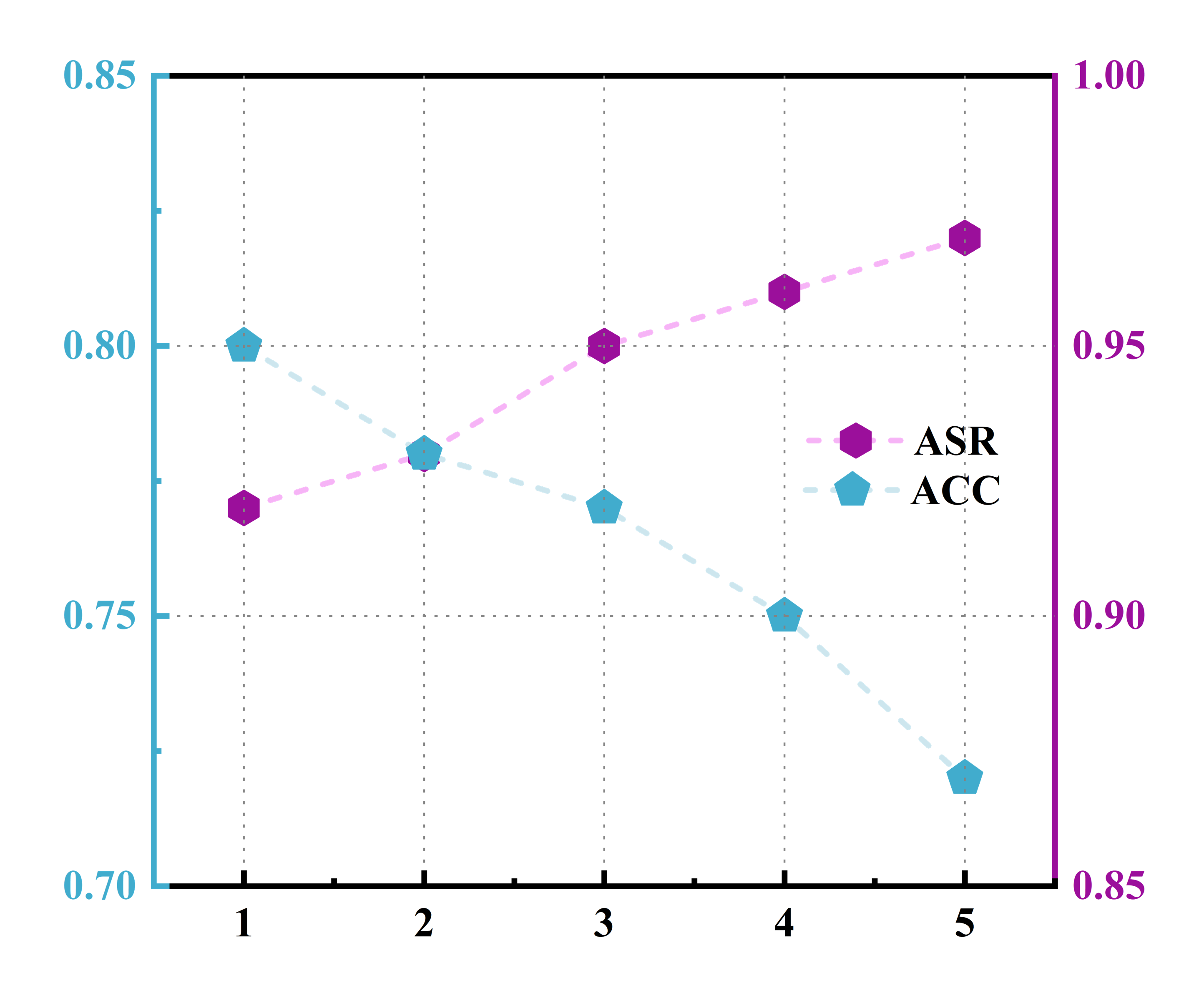
Researchers have uncovered a sophisticated attack that exploits attention mechanisms in federated self-supervised learning to inject hidden backdoors into models.