Author: Denis Avetisyan
This review explores a novel framework for optimizing security and energy efficiency in Open RAN networks as we transition to a post-quantum cryptographic landscape.
Energy-aware cryptographic scheduling within the Near-RT RIC minimizes consumption while ensuring security and latency requirements in O-RAN.
The increasing flexibility of Open Radio Access Networks (O-RAN) introduces new security challenges, particularly in light of the approaching threat of quantum computing. This paper, ‘Solving the Post-Quantum Control Plane Bottleneck: Energy-Aware Cryptographic Scheduling in Open RAN’, proposes an energy-aware framework leveraging the Near-RT RIC to intelligently schedule post-quantum cryptographic handshakes, minimizing energy consumption without compromising latency or security. Through batching, session resumption, and strategic parameter selection, the architecture demonstrably reduces per-handshake energy expenditure by up to 60%-but can these optimization techniques be extended to address the broader energy demands of future 5G and 6G networks?
The Inevitable Quantum Shadow: Securing Networks Before It’s Too Late
The foundation of modern digital security rests upon cryptographic algorithms – mathematical processes that scramble data to prevent unauthorized access. However, these widely used methods, such as RSA and ECC, are increasingly susceptible to a looming threat: quantum computers. Unlike classical computers that store information as bits representing 0 or 1, quantum computers leverage the principles of quantum mechanics to utilize qubits. These qubits can represent 0, 1, or a superposition of both, enabling exponentially faster computation for certain problems. Specifically, Shor’s algorithm, executable on a sufficiently powerful quantum computer, can efficiently factor large numbers – the mathematical basis of RSA – and break the elliptic curve cryptography that secures much of today’s internet traffic. This creates a critical security gap, as sensitive data currently protected by these algorithms could be decrypted and compromised once quantum computers reach a scale capable of running these attacks. The implications extend to all sectors relying on secure communication, from financial institutions and governments to healthcare providers and individual users.
The pervasive nature of current encryption algorithms means a widespread vulnerability exists across all digital communication networks. Cellular networks, reliant on secure authentication and data transmission, face potential compromise, as do the massive data centers that underpin cloud computing and global finance. This isn’t limited to high-profile targets; everyday internet browsing, email exchanges, and even critical infrastructure like power grids depend on these potentially breakable codes. Consequently, a reactive approach is insufficient; proactive solutions are urgently needed to assess vulnerabilities, develop and implement quantum-resistant algorithms, and establish new security protocols before the advent of sufficiently powerful quantum computers renders existing systems obsolete and exposes sensitive information on a global scale.
The move to Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) represents a paradigm shift, exceeding the scope of typical security updates. Existing encryption relies on mathematical problems considered intractable for classical computers, but quantum computers, leveraging principles of quantum mechanics, threaten to solve these problems efficiently. Consequently, PQC doesn’t simply refine current systems; it necessitates a complete overhaul of cryptographic algorithms and infrastructure. This transition involves adopting new mathematical approaches-like lattice-based cryptography, code-based cryptography, and multivariate cryptography-designed to resist attacks from both classical and quantum computers. The implications extend beyond simply protecting data; it’s about preserving the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of digital communications in a future where current security measures are fundamentally compromised, requiring proactive implementation and long-term strategic planning.
Orchestrating Quantum Resilience: A Two-Tiered RIC Approach
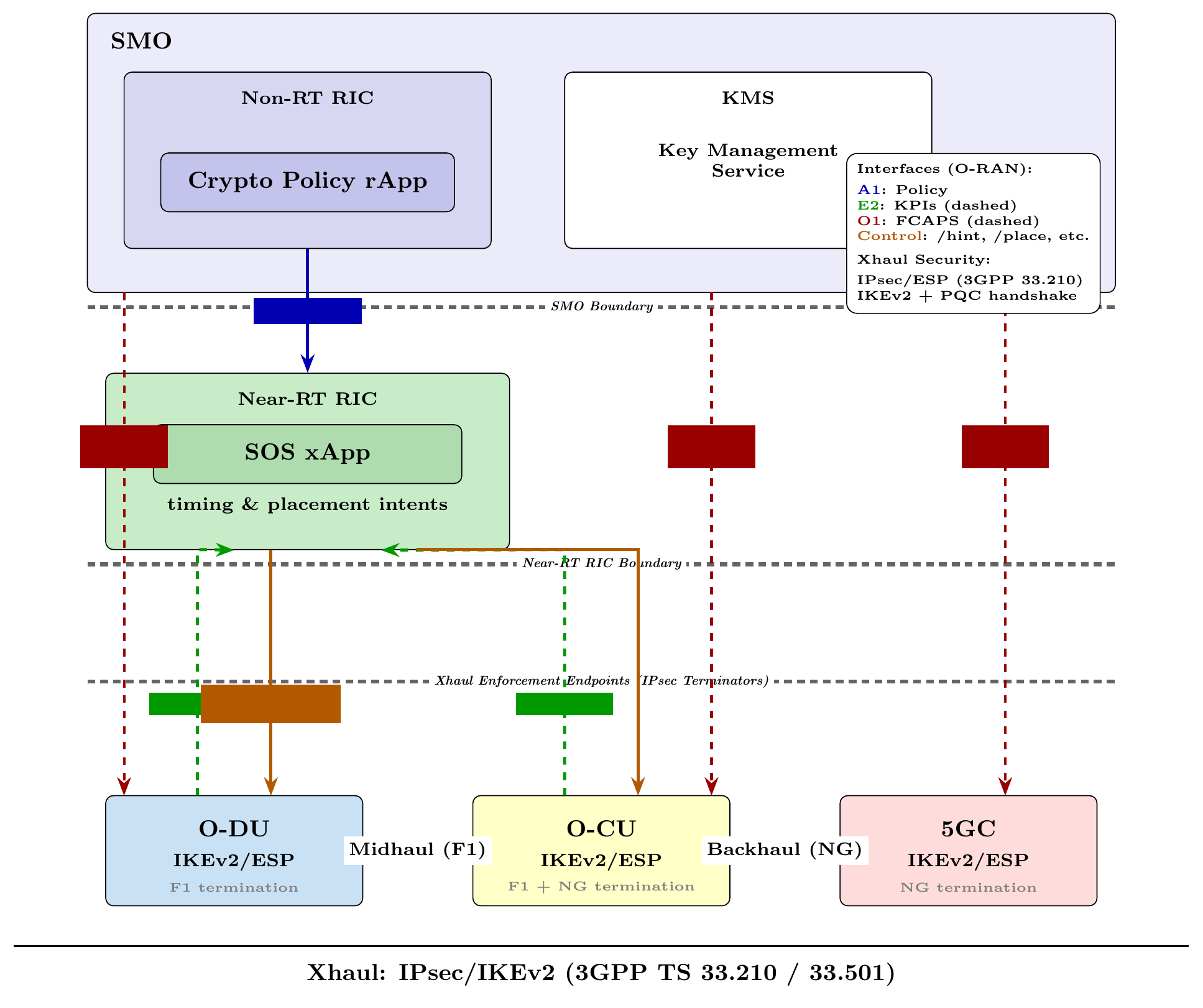
The O-RAN architecture facilitates Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) deployment by leveraging the capabilities of the Near-Real-Time (Near-RT) and Non-Real-Time (Non-RT) Radio Intelligent Controllers (RICs). This disaggregated approach allows for centralized control and distributed execution of cryptographic functions. The Non-RT RIC provides a platform for policy-based management, defining the overall PQC strategy, while the Near-RT RIC enables rapid, data-driven adaptation of cryptographic algorithms based on real-time network conditions and security requirements. This separation allows operators to update cryptographic suites without requiring changes to the radio access network hardware itself, increasing agility and reducing operational expenditure.
The Non-RT Radio Intelligent Controller (RIC) hosts the Crypto Policy Radio Application (rApp), which defines the high-level policies governing Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) suite deployment within the network. This rApp operates on a timescale of minutes to days, allowing it to consider network-wide factors such as operator preferences, regulatory requirements, and long-term security assessments. Specifically, the Crypto Policy rApp determines which PQC algorithms are permissible for use, and under what conditions – including key rotation schedules and algorithm agility parameters. These policies are then communicated to the Near-RT RIC, forming the basis for real-time security orchestration and ensuring consistent application of PQC across the network.
The Near-RT RIC’s Security Operations Scheduling (SOS) xApp functions as the execution layer for PQC policies defined in the Non-RT RIC. It receives the strategic policy envelope and translates it into real-time, tactical decisions regarding cryptographic algorithm selection and key management. This enables dynamic adaptation to changing security threats or network conditions; the SOS xApp can, for example, prioritize specific PQC algorithms based on observed attack patterns or adjust key rotation frequencies based on network load. The xApp operates by scheduling and controlling the execution of security functions within the RAN, effectively implementing the higher-level policies with low latency and granular control.
Squeezing Every Joule: Energy-Aware PQC Optimization
The Secure Orchestration Service (SOS) xApp employs Constrained Reinforcement Learning (RL) to optimize energy consumption for each secure connection. This optimization is achieved by dynamically adjusting Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) parameters based on real-time Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) received via E2SM-KPM signals. The RL agent is trained to minimize joules per secure connection, factoring in metrics such as computational load, network conditions, and security requirements as reported by the E2SM-KPM interface. This data-driven approach allows the SOS xApp to adapt to fluctuating network conditions and resource availability, ensuring efficient energy utilization without compromising security.
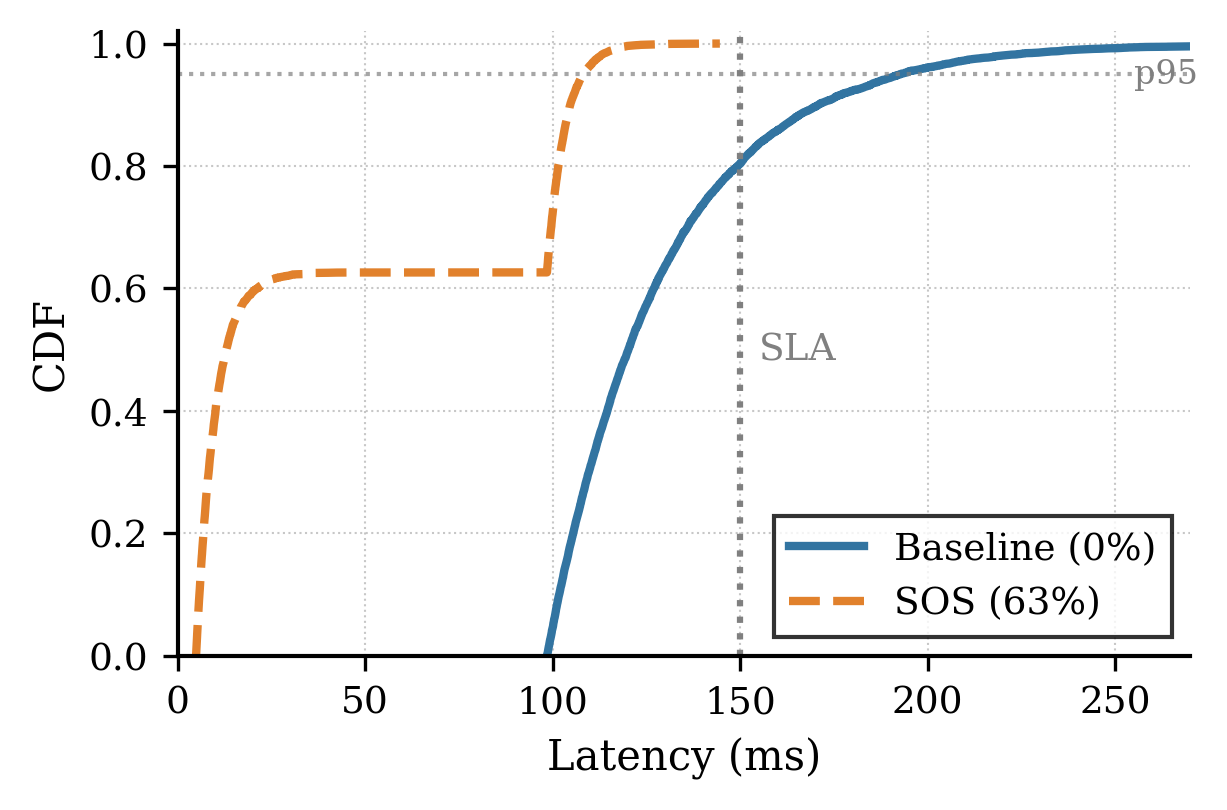
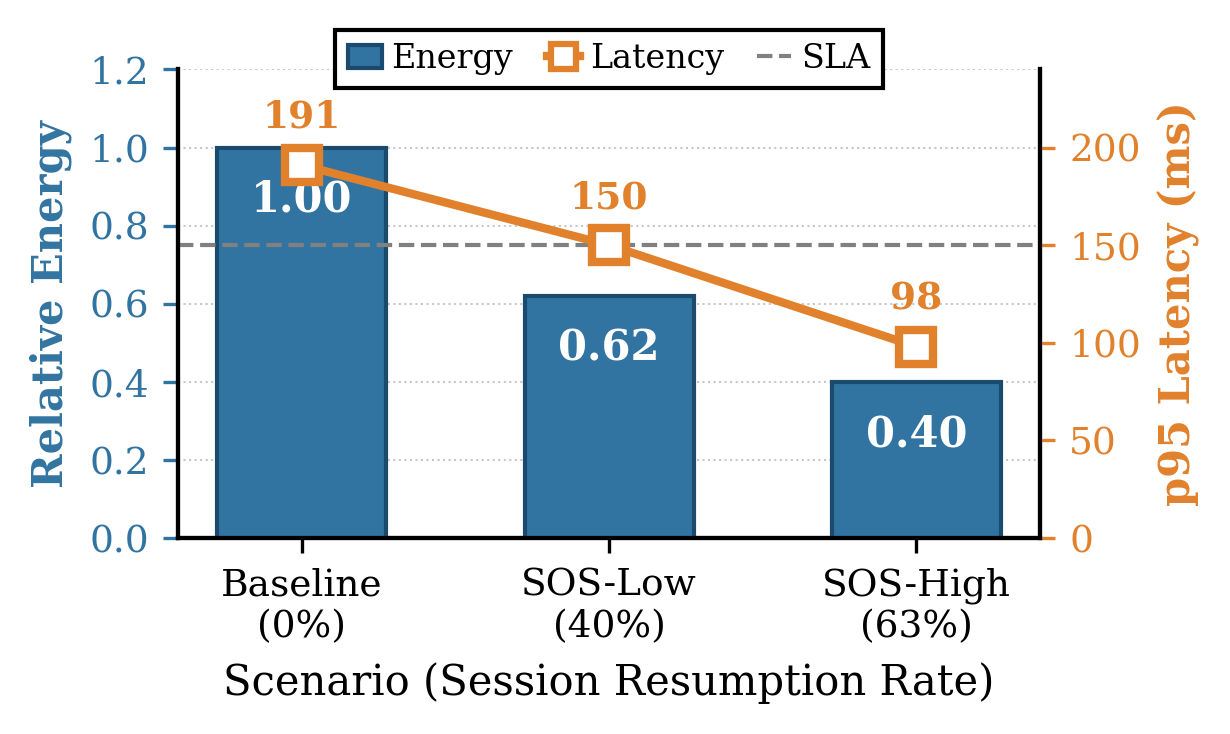
Adaptive Suite Selection, implemented within the SOS xApp, utilizes a Constrained Reinforcement Learning policy to dynamically choose Post-Quantum Cryptographic (PQC) suites and hardware accelerators on a per-connection basis. This selection process is driven by real-time data received via E2SM-KPM signals, allowing the system to prioritize energy efficiency without compromising security. Testing demonstrates this approach achieves up to a 60% reduction in energy consumption while maintaining a 63% session resumption rate, minimizing the overhead associated with frequent key exchanges and cryptographic operations.
Handshake scheduling optimizes resource utilization by aligning rekeying operations with periods of reduced network activity. This strategic timing significantly decreases handshake service time to 4.92 milliseconds, representing a substantial improvement over the 98.48 milliseconds required for standard, full handshakes. The reduction in handshake duration minimizes processing overhead and conserves network resources, contributing to overall system efficiency. This approach avoids peak load conditions during rekeying, maintaining consistent performance and reducing latency for secure connections.
Fortifying the O-RAN Fabric: End-to-End Protection
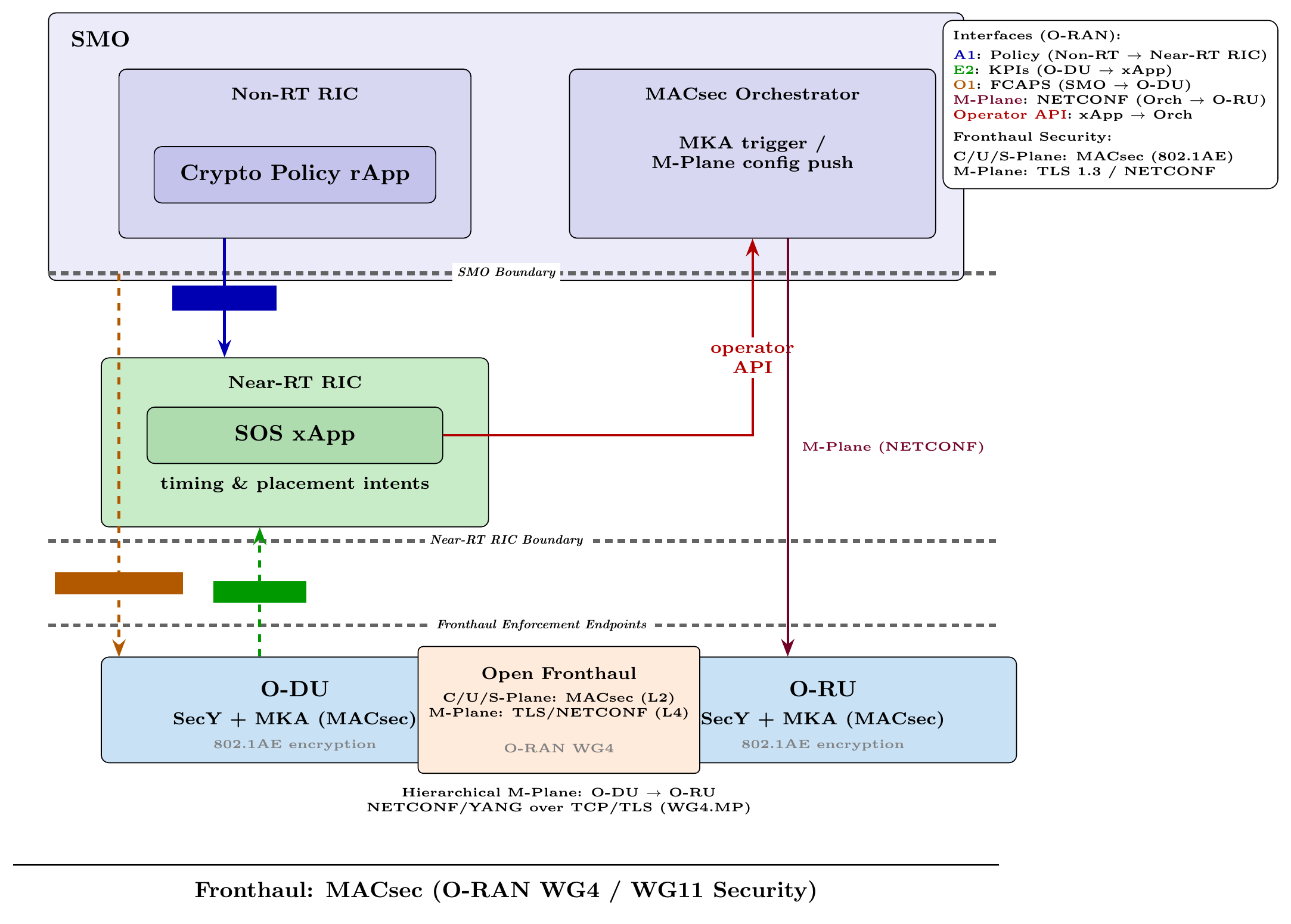
The implementation of Media Access Control Security (MACsec) throughout the Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) architecture delivers critical link-layer protection. By securing communication pathways between the O-Radio Unit (O-RU), the O-Distribution Unit (O-DU), and the vital F1 interface, MACsec establishes encrypted connections that safeguard data integrity and confidentiality. This approach fortifies the network against eavesdropping and manipulation, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected as it traverses between these key components. Utilizing cryptographic keys and secure authentication mechanisms, MACsec effectively creates a trusted layer at the physical level, bolstering the overall security posture of the O-RAN deployment and minimizing potential vulnerabilities inherent in wireless communication systems.
The implementation of Zero Trust principles within the O-RAN architecture establishes a security paradigm where no user or device is implicitly trusted, demanding stringent verification before granting access to network resources. This is achieved through the synergistic application of MACsec and IPsec, cryptographic protocols that secure data in transit and at rest, respectively. By enforcing cryptographic control at standards-compliant endpoints – the O-RU, O-DU, and interfaces between them – the system ensures that all communication is authenticated and encrypted. This granular level of security minimizes the attack surface and prevents unauthorized access, effectively validating every access request and continuously monitoring network activity for potential threats, bolstering the overall resilience of the O-RAN infrastructure.
A comprehensive security implementation, leveraging end-to-end encryption and the SOS framework, demonstrably elevates service reliability within O-RAN deployments. Rigorous testing reveals a substantial increase in Service Level Agreement (SLA) compliance, reaching 98.2%. This represents a significant improvement over a previously measured baseline of 85.7%, indicating a marked reduction in service disruptions and a heightened capacity to meet committed performance metrics. The data suggests that proactive security measures are not merely preventative, but directly contribute to a more stable and dependable network infrastructure, fostering increased operator confidence and improved user experiences.
Beyond Encryption: Adaptability and Efficiency in Future Networks
The convergence of Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC), intelligent Radio Intelligent Controller (RIC) applications, and strengthened security protocols is forging a new paradigm in network resilience. Traditional cryptographic methods face imminent threats from quantum computing advancements, necessitating the implementation of PQC algorithms to safeguard data integrity and confidentiality. However, simply adopting new cryptography isn’t enough; intelligent RIC applications dynamically optimize network resources, ensuring security measures don’t compromise performance. This is achieved through real-time threat analysis and adaptive security policies. By layering robust security protocols – encompassing authentication, encryption, and access control – on top of this intelligent and quantum-resistant foundation, networks can not only withstand current attacks but also proactively adapt to evolving threats, ensuring a future-proof infrastructure capable of supporting increasingly complex and data-intensive applications.
Network performance gains are increasingly achieved through session resumption techniques, which minimize the computational burden of repeated handshakes. Rather than fully renegotiating secure connections for each data transfer, systems can leverage pre-shared keys (PSK) and similar mechanisms to verify identity and establish encryption with significantly reduced overhead. This approach dramatically lowers latency and conserves bandwidth, particularly crucial for resource-constrained devices and applications demanding real-time responsiveness. By caching authentication data and intelligently reusing session keys, networks can maintain robust security while simultaneously optimizing efficiency, paving the way for scalable and reliable communication in dynamic environments.
The convergence of advanced network security isn’t merely about safeguarding data; it’s a foundational requirement for realizing the full potential of next-generation technologies. Massive Internet of Things deployments, envisioning billions of interconnected devices, demand streamlined security protocols that minimize overhead and maximize scalability. Simultaneously, applications requiring ultra-reliable low-latency communication – such as autonomous vehicles and remote surgery – necessitate consistently secure and near-instantaneous connections. This integrated framework, built on post-quantum cryptography and intelligent network control, provides the necessary responsiveness and resilience to support these demanding applications, ensuring data integrity and system availability even in the face of evolving cyber threats and exponentially increasing network complexity. It represents a proactive shift from securing existing infrastructure to enabling the future of connected systems.
The pursuit of elegant solutions in O-RAN, particularly regarding post-quantum cryptography, feels less like innovation and more like delaying the inevitable entropy. This paper attempts to sculpt order from the chaos of near real-time RIC functions, focusing on energy-aware scheduling. It’s a valiant effort, yet one can’t help but suspect it merely shifts the pressure points. Blaise Pascal observed, “All of humanity’s problems stem from man’s inability to sit quietly in a room alone.” Translated to this context, it suggests the fundamental problem isn’t how to schedule cryptographic operations, but the relentless demand for ever-increasing complexity. The bug tracker will, inevitably, fill with variations on this theme. They don’t deploy – they let go.
Future-Proofing the Inevitable
This work, predictably, addresses a problem created by solving another. The transition to post-quantum cryptography within O-RAN-a laudable goal-introduces a fresh set of energy and scheduling concerns. It’s a comforting pattern: fix one bottleneck, discover three more. The proposed framework offers a temporary reprieve, a meticulously crafted bandage on a system inherently prone to entropy. One suspects that as quantum computing matures, the energy savings realized through clever scheduling will be dwarfed by the sheer computational cost of the cryptography itself.
The real challenge, glossed over in most ‘future-proof’ architectures, isn’t the algorithm, but the scale. Deploying this, or any similar orchestration, across a truly heterogeneous network will reveal unforeseen interactions. The assumption of predictable session resumption, while elegant in simulation, will encounter the chaotic reality of user behavior and network congestion.
Ultimately, this is another layer of complexity atop a network already drowning in them. It’s not about building a secure system; it’s about building a system that fails gracefully, and ideally, leaves legible error messages for the digital archaeologists who will dissect it decades hence. Perhaps future work should focus less on optimization and more on robust failure modes-if a system crashes consistently, at least it’s predictable.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2602.11820.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- EUR USD PREDICTION
- Epic Games Store Free Games for November 6 Are Great for the Busy Holiday Season
- How to Unlock & Upgrade Hobbies in Heartopia
- Battlefield 6 Open Beta Anti-Cheat Has Weird Issue on PC
- Sony Shuts Down PlayStation Stars Loyalty Program
- TRX PREDICTION. TRX cryptocurrency
- The Mandalorian & Grogu Hits A Worrying Star Wars Snag Ahead Of Its Release
- Xbox Game Pass September Wave 1 Revealed
- INR RUB PREDICTION
- Best Ship Quest Order in Dragon Quest 2 Remake
2026-02-13 10:17