Author: Denis Avetisyan
Researchers are developing methods to identify and prioritize smart contract audits by analyzing patterns of code obfuscation that drift across different blockchain ecosystems.
This paper presents a scalable cross-chain analysis of smart contract obfuscation, leveraging structural features and template reuse to improve audit prioritization and security.
Smart contract security auditing is increasingly challenged by obfuscation techniques, yet the consistency and transferability of obfuscation signals across different blockchains remain largely unaddressed. This paper, ‘From Scores to Queues: Operationalizing Cross-Chain Obfuscation Signals for Smart-Contract Audits’, presents HObfNET, a scalable model for cross-chain analysis that reveals systematic drift in obfuscation scores and prioritizes audit queues based on structural bytecode features and template reuse. Our findings demonstrate that high-score contracts exhibit distinct characteristics-rare selectors, external calls, and low signature density-and that publicly known security incidents consistently appear within the highest-risk queue. Can this approach to cross-chain linkage and audit prioritization fundamentally reshape multi-chain security operations and proactively mitigate emerging threats?
The Illusion of Control: Smart Contracts and the Rise of Obfuscation
The promise of smart contracts – self-executing agreements on blockchains – is increasingly shadowed by a surge in malicious activity. Attackers are no longer solely focused on exploiting coding errors; instead, they are proactively employing obfuscation techniques to conceal the true intent of their contracts. This deliberate masking involves transforming the contract’s bytecode, essentially scrambling the instructions to make analysis significantly more difficult. While the underlying functionality may remain the same, the altered code presents a deceptive facade, hindering security professionals and automated tools from accurately identifying vulnerabilities. This escalating trend represents a fundamental shift in the threat landscape, demanding a more sophisticated approach to smart contract security than simply searching for bugs in legible code.
Malicious actors are increasingly employing deliberate bytecode transformations to conceal the true functionality of smart contracts, effectively creating a smokescreen for exploitable vulnerabilities. These transformations, which alter the contract’s code without changing its external behavior, introduce significant challenges for security auditors who rely on readable, understandable code to identify flaws. By obscuring the underlying logic, these techniques make it substantially more difficult to detect hidden backdoors, malicious logic, or subtle bugs that could be exploited by attackers. This intentional complexity not only increases the time and resources required for effective audits, but also raises the likelihood that vulnerabilities will remain undetected, posing a growing threat to the security and reliability of decentralized applications and the funds they manage.
The increasing sophistication of smart contract obfuscation presents a significant challenge to conventional security analysis. Existing tools, designed to interpret readily understandable bytecode, falter when confronted with deliberately convoluted code-transformations like instruction substitution, opaque predicates, and control flow flattening effectively mask the contract’s true intent. This hinders static analysis, making it difficult to verify functionality and identify vulnerabilities, while dynamic analysis is complicated by the increased execution time and state space required to observe the contract’s behavior. Consequently, researchers are actively developing novel approaches, including symbolic execution, machine learning-based anomaly detection, and formal verification techniques tailored to handle obfuscated code, in an effort to restore confidence in the security of decentralized applications.
HObfNET and ObfProbe: A Scalable Approach to Obfuscation Detection
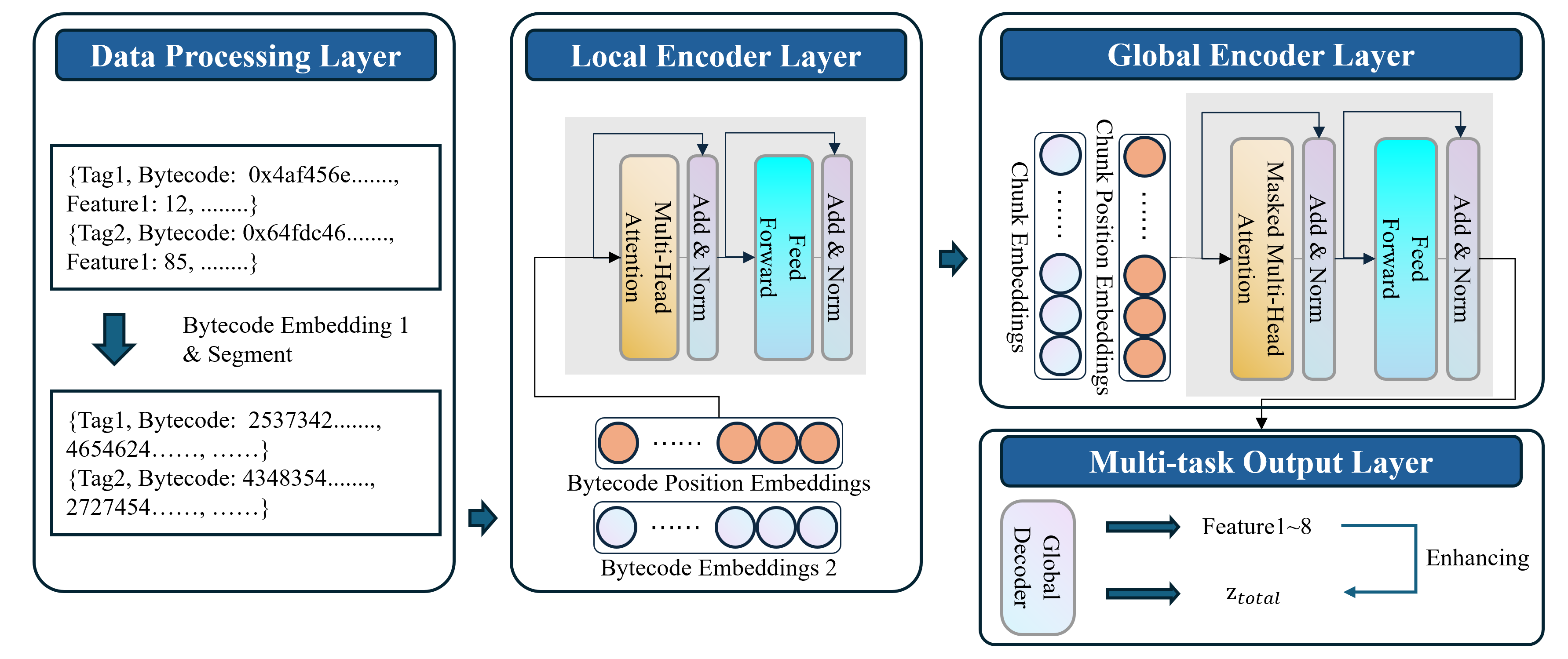
HObfNET is a hierarchical attention network developed to provide a computationally efficient alternative to comprehensive bytecode analysis. The network is designed to process features extracted directly from smart contract bytecode, enabling scalable assessment of code obfuscation levels. Its hierarchical structure allows it to focus on the most relevant bytecode characteristics, significantly reducing processing time while maintaining a high degree of accuracy. Inference speeds are consistently measured at 8-9 milliseconds per contract, representing a substantial performance improvement over traditional bytecode analysis methods and enabling rapid evaluation of large codebases.
HObfNET utilizes features directly derived from smart contract bytecode to generate obfuscation scores, enabling scalable analysis of large contract sets. The network’s architecture is designed for rapid inference, consistently achieving processing speeds of 8-9 milliseconds per contract. This performance is achieved through feature extraction from the bytecode, which allows for a computationally efficient assessment of obfuscation levels without requiring full bytecode disassembly or complex static analysis techniques. The resulting scores provide a quantitative metric for gauging code complexity and identifying potentially malicious or intentionally obscured contracts.
ObfProbe is a tool designed to quantify obfuscation specifically within contract transfer paths by employing a feature ranking methodology. This process identifies and scores characteristics indicative of obfuscation techniques. HObfNET builds upon this foundation, providing a significantly improved performance profile; specifically, HObfNET achieves a speed increase of 2,300 to 5,200 times faster execution compared to the second-level analysis runs within ObfProbe. This acceleration allows for scalable analysis of larger codebases while retaining the core functionality of transfer-path obfuscation quantification established by the original ObfProbe tool.
The integrated HObfNET and ObfProbe system enables efficient evaluation of smart contract code complexity and the identification of contracts exhibiting significant obfuscation. Quantitative analysis demonstrates a high degree of accuracy, with a Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) of 8.20% when compared against the original, more computationally intensive ObfProbe. Furthermore, a Pearson Correlation Coefficient (PCC) of 0.9158 confirms a strong positive correlation between the obfuscation scores generated by the combined system and those produced by the baseline ObfProbe methodology, validating the reliability of the faster assessment process.
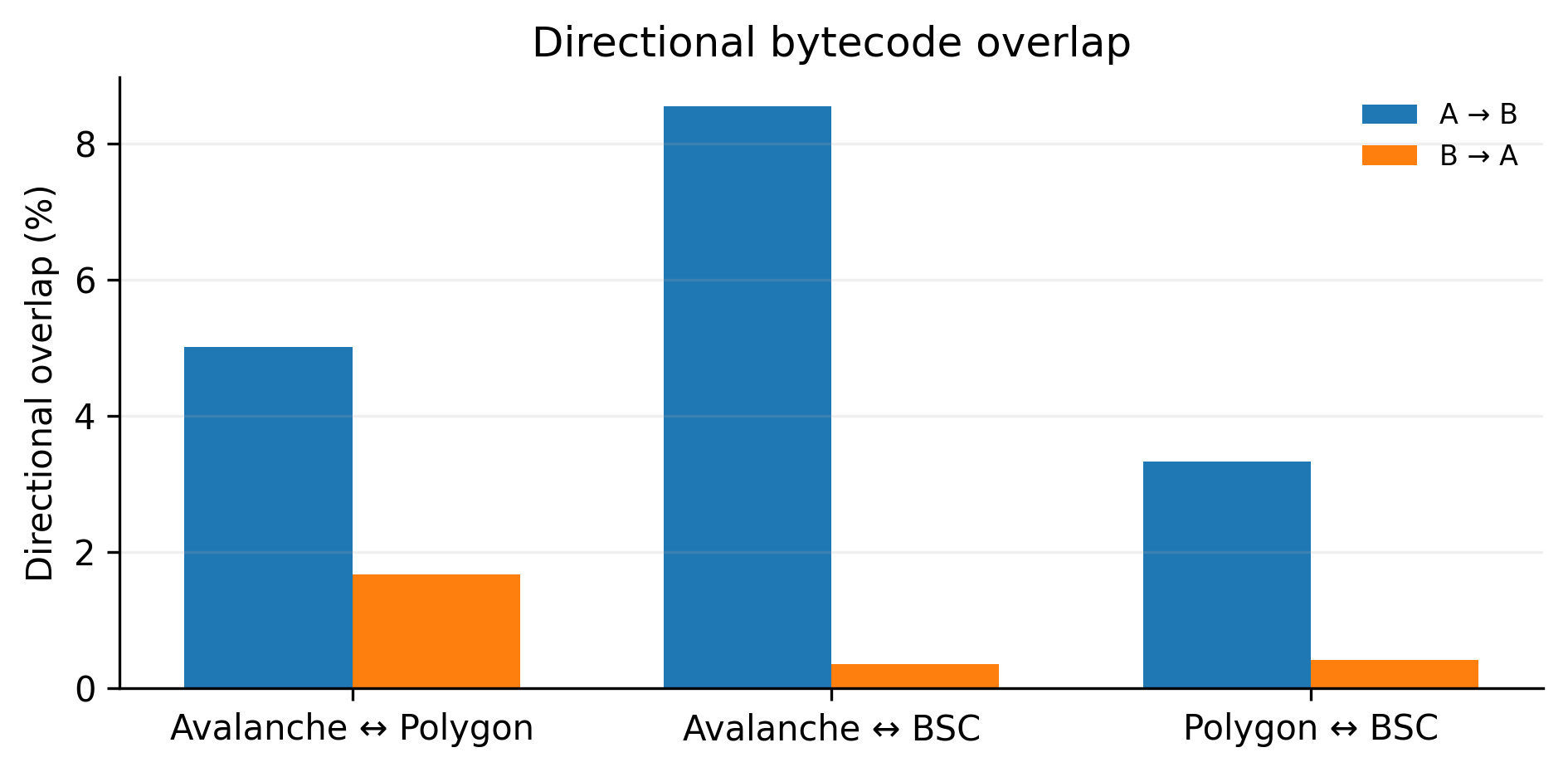
Cross-Chain Shadows: Uncovering Patterns of Obfuscation
Our analytical framework incorporates cross-chain investigation, specifically examining smart contract deployments on Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain (BSC), Polygon, and Avalanche. This multi-chain approach allows for the identification of contract similarities and potential relationships that would be obscured by analyzing a single blockchain in isolation. Data is collected from each network regarding contract creation, bytecode, and on-chain interactions, and is then normalized for comparative analysis. The scope includes both directly deployed contracts and those accessed through cross-chain communication protocols, facilitating a comprehensive view of asset and data flow across these layer-1 and layer-2 ecosystems.
Cross-chain reuse refers to the practice of deploying identical or near-identical smart contract code across multiple blockchain platforms, including Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain (BSC), Polygon, and Avalanche. Our analysis identifies these instances by comparing contract bytecodes, even when subjected to obfuscation techniques intended to hinder identification. The prevalence of cross-chain reuse suggests a deliberate strategy employed by developers, potentially to rapidly deploy functionality across different ecosystems or to exploit vulnerabilities common to multiple chains. Detection relies on identifying contracts with high levels of similarity despite variations introduced by platform-specific compilation or obfuscation processes.
Analysis of obfuscated smart contracts reveals the presence of ‘external call enrichment’ and the utilization of ‘rare selectors’. External call enrichment refers to contracts that initiate a disproportionately high number of calls to other contracts, potentially indicating attempts to manipulate external state or exploit vulnerabilities within those contracts. Rare selectors, those infrequently observed across the broader smart contract landscape, suggest developers are employing custom or specialized logic, potentially to evade detection or implement unique malicious functionality. The co-occurrence of these features within obfuscated contracts raises concerns about complex interactions and heightened risk, necessitating further investigation to determine intent and potential impact.
Signature density, a metric quantifying the number of unique function selectors within a smart contract, serves as an indicator of code complexity and potential vulnerability surfaces. Our analysis demonstrates that contracts exhibiting high levels of obfuscation – comprising the ‘high-obfuscation tail’ – display a Tail Jaccard Index that is 1.5 to 2.0 times greater than the average across all analyzed contracts. This elevated index indicates a significantly higher degree of cross-chain reuse of code components within these obfuscated contracts, suggesting that these contracts are not uniquely developed for each chain but rather deployed with substantial code replication across Ethereum, BSC, Polygon, and Avalanche.
Beyond Detection: Implications for Security and Future Research
Automated analysis of code obfuscation in smart contracts is now demonstrably feasible, providing a significant advancement for those tasked with ensuring blockchain security. This research introduces a method to systematically identify and assess the degree of obfuscation within contract code, offering a crucial tool for security auditors and vulnerability researchers who often rely on manual inspection – a process that is both time-consuming and prone to error. By automating this process, potential security weaknesses hidden by deliberate code complexity can be flagged more efficiently, enabling proactive risk assessment and targeted interventions before vulnerabilities are exploited. The ability to rapidly analyze a contract’s obfuscation level not only streamlines the security auditing workflow but also facilitates a more comprehensive understanding of the threat landscape within decentralized applications.
The capacity to pinpoint and categorize obfuscated smart contracts represents a significant leap towards preventative security measures. By establishing a clear ranking of contracts based on the degree of obfuscation, security professionals gain the ability to prioritize audits and focus investigative efforts on those posing the highest potential risk. This proactive approach allows for targeted interventions, such as deeper code reviews or dynamic analysis, before vulnerabilities can be exploited. Rather than reacting to breaches, this methodology facilitates a shift towards preemptive risk mitigation, ultimately strengthening the overall resilience of the blockchain ecosystem and fostering greater trust in decentralized applications.
Continued investigation into automated obfuscation analysis necessitates a broadening of current methodologies and their application to the rapidly evolving landscape of blockchain technologies. Future work should prioritize the development of more robust and adaptable algorithms capable of discerning increasingly sophisticated obfuscation techniques employed across diverse platforms. Expanding the scope beyond currently analyzed chains – Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Polygon, and Avalanche – to include emerging architectures and layer-2 solutions is crucial for comprehensive security assessments. Such research will not only refine the accuracy of identifying malicious code but also facilitate proactive vulnerability discovery, ultimately contributing to a more secure and resilient smart contract ecosystem as blockchain technology continues to mature and proliferate.
A robust and dependable smart contract ecosystem hinges on a comprehensive grasp of code obfuscation techniques. Recent analysis demonstrates that identifying obfuscated contracts is not simply a matter of applying a single, universal threshold; instead, optimal detection values vary significantly between different blockchain networks. Specifically, the research reveals chain-specific thresholds for identifying potentially malicious obfuscation, with Ethereum registering at 18.07, Binance Smart Chain at 16.82, Polygon at 18.72, and Avalanche at 19.18. These findings underscore the critical need for tailored security assessments that account for the nuances of each blockchain’s environment, moving beyond generalized approaches to ensure more effective vulnerability detection and a more resilient decentralized landscape.
The pursuit of automated audit prioritization, as detailed in the analysis of cross-chain obfuscation, feels predictably Sisyphean. This work attempts to quantify ‘drift’ in obfuscation scores – essentially, tracking how quickly clever defenses become transparent – and build a system to react. As Ken Thompson famously observed, “Debugging is twice as hard as writing the code in the first place. Therefore, if you write the code as cleverly as possible, you are, by definition, not smart enough to debug it.” The same logic applies here. Each attempt to automate security, to build a ‘temple’ of CI around predictable patterns of obfuscation, simply creates a new, more complex surface for entropy to exploit. The researchers identify template reuse, a form of predictable structure, and build upon it. It’s a useful step, naturally, but one destined to become tomorrow’s technical debt, as production inevitably uncovers the limitations of even the most carefully constructed systems.
What’s Next?
The pursuit of scalable cross-chain obfuscation analysis feels… familiar. It began, as these things always do, with a simple bash script and a fervent hope that ‘interesting’ contracts would stand out. Now, it’s become a system of queues and scores, predictably. The drift in obfuscation scores identified in this work isn’t groundbreaking; entropy increases. What’s concerning is the inevitability of someone branding this ‘AI-powered audit prioritization’ and securing a Series A. They’ll call it proactive security, and conveniently forget that template reuse, while efficient for attackers, was always the real problem.
Future work will, naturally, focus on automating the detection of these templates. This will create a cat-and-mouse game of increasing complexity, with the ‘mouse’ eventually being a disgruntled developer tasked with manually reviewing the output of yet another machine learning model. The core issue isn’t the obfuscation itself, but the fundamental fragility of code designed for financial incentives. It’s a lesson learned, then promptly forgotten, with each new chain.
Perhaps the next iteration will involve predicting where obfuscation will be deployed, based on gas prices and market volatility. Or, more likely, someone will simply increase the training data and hope for the best. The documentation will lie again, promising perfect detection, and the cycle will continue. It’s not a technical limitation, really. It’s just emotional debt with commits.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2601.17356.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Enshrouded: Giant Critter Scales Location
- All Carcadia Burn ECHO Log Locations in Borderlands 4
- Best Finishers In WWE 2K25
- Best ARs in BF6
- Top 10 Must-Watch Isekai Anime on Crunchyroll Revealed!
- Poppy Playtime 5: Battery Locations & Locker Code for Huggy Escape Room
- All Shrine Climb Locations in Ghost of Yotei
- Best Anime Cyborgs
- Keeping Agents in Check: A New Framework for Safe Multi-Agent Systems
- Top 8 UFC 5 Perks Every Fighter Should Use
2026-01-27 17:49