Author: Denis Avetisyan
A new method previews future data to significantly improve the compression of large language models without sacrificing accuracy.
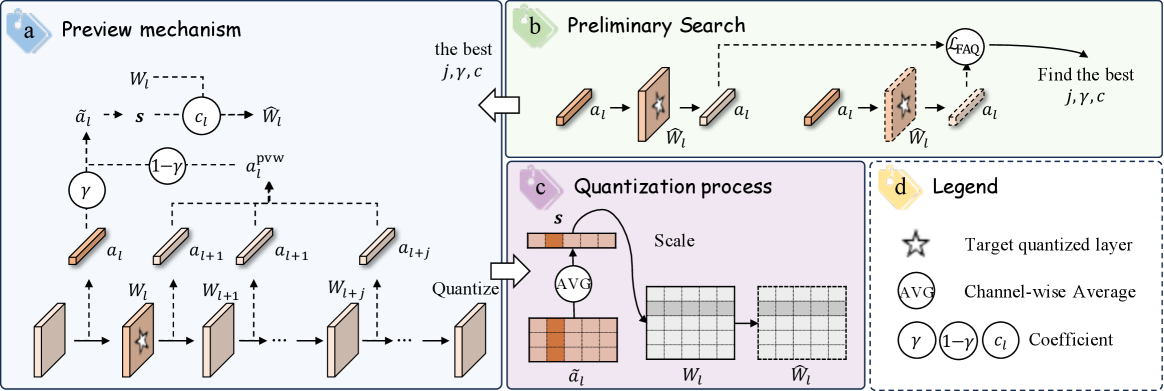
Future-Aware Quantization addresses quantization bias and error accumulation to enable more efficient low-bit deployment.
Despite the success of post-training quantization (PTQ) for compressing large language models, current methods remain vulnerable to quantization bias and error accumulation, particularly when calibration data is imperfect. This paper, ‘Enhancing Post-Training Quantization via Future Activation Awareness’, introduces Future-Aware Quantization (FAQ), a novel approach that leverages activations from subsequent layers to guide the quantization process. By considering future information, FAQ better preserves important weights and reduces sensitivity to noisy calibration data, achieving improved performance without requiring fine-tuning or complex search procedures. Could this forward-looking strategy unlock even greater efficiencies in deploying large models on resource-constrained devices?
The Computational Imperative of Large Language Models
The recent surge in capabilities demonstrated by Large Language Models (LLMs) – exemplified by architectures like Qwen and LLaMA – comes at a considerable cost. These models, while achieving state-of-the-art performance on various natural language processing tasks, require immense computational resources for both training and inference. The sheer scale of parameters – often numbering in the billions – translates directly into substantial memory requirements and processing demands. This presents a significant barrier to wider accessibility and deployment, particularly for resource-constrained environments or applications requiring real-time responsiveness. The intensive computational load not only limits who can effectively utilize these powerful tools, but also raises concerns about the environmental impact associated with their operation, driving research into more efficient model designs and compression techniques.
Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) presents a compelling strategy for reducing the immense computational demands of Large Language Models (LLMs), but achieving this compression without substantial performance loss remains a significant hurdle. Standard PTQ methods, including techniques like RTN (Round-to-Nearest) and AWQ (Activation-Aware Weight Quantization), aim to represent model weights and activations with fewer bits – typically moving from 16-bit or 32-bit floating-point numbers to 8-bit integers or even lower. While this dramatically reduces model size and accelerates inference, the process introduces quantization errors that can accumulate and degrade accuracy, particularly in complex LLMs. These errors arise from the inherent information loss when representing a continuous range of values with a limited number of discrete levels, and current PTQ techniques often struggle to minimize this loss without extensive, and computationally expensive, calibration or fine-tuning.
The process of reducing a large language model’s precision through layer-wise quantization, while intended to compress the model, can inadvertently introduce a phenomenon known as Quantization Bias. This occurs because each layer is optimized independently, leading to the disproportionate compression of important channels – those most critical for accurate predictions – while less vital channels remain relatively unaffected. Consequently, the model’s ability to discern subtle but crucial patterns diminishes, resulting in a noticeable drop in overall performance. This bias isn’t simply random error; it’s a systematic compression of the model’s most sensitive features, highlighting the need for quantization strategies that consider the holistic impact on all channels and layers rather than optimizing them in isolation.
Future-Aware Quantization: A Principled Solution
Future-Aware Quantization (FAQ) is a Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) technique that improves accuracy by incorporating information from activations in subsequent layers during the quantization process. Traditional PTQ methods independently quantize each layer, potentially leading to significant information loss. FAQ addresses this by considering the impact of quantization on downstream layers, effectively propagating sensitivity information backward through the network. This is achieved by utilizing activations from future layers to refine the quantization parameters of the current layer, resulting in a more globally optimized and accurate quantized model. The core principle is to minimize the cumulative quantization error across the entire network, rather than optimizing each layer in isolation.
The Window-Wise Preview mechanism within Future-Aware Quantization (FAQ) enhances layer-wise quantization by moving beyond purely local activation statistics. Instead of evaluating activations solely within a given layer, FAQ aggregates activation information from a preceding “window” of layers. This aggregation is performed “softly” through a weighted average, allowing the quantization process to consider the impact of downstream layers on the current layer’s optimal quantization parameters. By previewing future activations, the method aims to mitigate the error propagation common in post-training quantization and make more informed decisions regarding the scaling factors and zero points applied to each layer’s weights and activations.
The Activation-Aware Framework within Future-Aware Quantization (FAQ) operates by dynamically adjusting quantization parameters based on layer-specific activation distributions. This is achieved through statistical analysis of activations during a calibration phase, calculating metrics such as mean and standard deviation for each layer. These metrics are then used to refine the scaling factors and zero points applied during quantization, minimizing information loss and maintaining representational capacity. The framework ensures that layers with wider or more complex activation ranges receive finer-grained quantization, while those with simpler distributions can be quantized more aggressively, resulting in a more efficient and accurate model compression.
Future-Aware Quantization (FAQ) streamlines deployment by utilizing a pre-defined configuration derived from an extensive search across diverse models and datasets. This eliminates the need for per-model hyperparameter tuning during the post-training quantization (PTQ) calibration process, which is typically computationally expensive and time-consuming. The pre-searched configuration establishes optimal quantization parameters – including bit-widths and scaling factors – for each layer, ensuring high accuracy with minimal calibration overhead. This approach significantly reduces the engineering effort required for model deployment, making FAQ a practical solution for resource-constrained environments.
Empirical Validation: Demonstrating Quantifiable Gains
Empirical results demonstrate that the FAQ quantization method consistently surpasses the performance of baseline Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) techniques, specifically RTN and AWQ, across diverse datasets. Evaluations utilizing Perplexity as a metric show that on the Qwen2.5-0.5B model, FAQ achieves a Perplexity of 25.9575 on the WikiText2 dataset. This represents a quantifiable improvement over the 29.1318 Perplexity attained by the AWQ method on the same dataset and model, indicating a more accurate probability distribution prediction by the FAQ-quantized model.
Evaluations on commonsense reasoning benchmarks demonstrate performance gains with the FAQ method. Specifically, using the Qwen3-8B model, FAQ achieves an accuracy of 0.5043 on the ARC challenge dataset, representing an improvement over the 0.4778 accuracy obtained with AWQ. Similarly, on the PIQA benchmark, FAQ yields an accuracy of 0.7535 with Qwen3-8B, compared to 0.7459 achieved by AWQ. These results indicate that FAQ effectively enhances performance on tasks requiring commonsense understanding and reasoning capabilities.
Quantization, while reducing model size and increasing inference speed, introduces Quantization Bias and Error Accumulation that degrade performance. FAQ addresses these issues by employing a novel quantization scheme that minimizes the discrepancy between full-precision and quantized weights and activations. This mitigation results in more robust models less susceptible to the performance loss typically associated with reduced precision, leading to improved accuracy and reliability across various tasks and datasets. By reducing the impact of quantization artifacts, FAQ maintains a higher level of representational fidelity, allowing models to generalize more effectively and consistently.
Asymmetric quantization within the FAQ method improves model performance by accommodating the non-uniform distribution of activation values. Evaluations on the BoolQ benchmark demonstrate this enhancement; FAQ achieves an accuracy of 0.8529 when applied to the Qwen3-8B model. Furthermore, at a 3-bit quantization level on the Qwen2.5-0.5B model, FAQ yields a +1.14% increase in BoolQ accuracy compared to baseline quantization techniques, indicating an increased ability to retain information during the reduction of model precision.
Expanding the Horizon: Implications and Future Trajectories
Future-Aware Quantization (FAQ) presents a pragmatic approach to deploying large language models on devices with limited computational resources. This technique strategically compresses models – reducing their size and energy consumption – without substantially sacrificing performance. By intelligently managing the quantization process, FAQ preserves critical information within the model, enabling effective natural language processing capabilities on smartphones, embedded systems, and other resource-constrained platforms. The innovation effectively democratizes access to advanced AI, extending the benefits of LLMs beyond powerful servers and into everyday applications, and fostering a more sustainable AI ecosystem through reduced computational demands.
The development of FAQ facilitates a paradigm shift in large language model deployment, moving beyond the limitations of substantial computational resources. By enabling efficient inference – the process of using a trained model to make predictions – on resource-constrained devices, this technique democratizes access to advanced natural language processing capabilities. Critically, reduced computational demands translate directly into lower energy consumption during both training and inference phases. This decrease in energy use has significant implications for mitigating the environmental impact of increasingly prevalent AI systems, actively reducing the carbon footprint associated with large-scale model deployment and fostering a more sustainable approach to artificial intelligence.
Researchers are actively broadening the applicability of future-awareness quantization (FAQ) beyond its initial implementation, with ongoing investigations targeting diverse model architectures like transformers and convolutional neural networks. This expansion aims to establish FAQ as a broadly useful compression technique, not limited to a specific model type. Simultaneously, efforts are focused on developing adaptive quantization strategies that dynamically adjust the precision of model weights based on their sensitivity, potentially yielding even greater compression ratios without sacrificing accuracy. These adaptive methods promise to refine the balance between model size, computational efficiency, and performance, ultimately paving the way for deploying increasingly sophisticated AI models on a wider range of hardware platforms and reducing the energy demands of large-scale inference.
Researchers are actively investigating synergistic combinations of future-awareness – a technique anticipating upcoming data needs during compression – with established optimization methods like quantization and pruning. This pursuit isn’t merely about shrinking model size; it’s a drive to fundamentally redefine the limits of efficient artificial intelligence. By intelligently forecasting future computational demands, these combined approaches promise to minimize performance degradation during compression, enabling deployment on previously inaccessible hardware. This advancement isn’t limited to specific applications; it lays the groundwork for a new generation of AI systems that are both powerful and remarkably resource-conscious, potentially unlocking breakthroughs in areas ranging from personalized medicine to real-time environmental monitoring and beyond.
The pursuit of efficient large language models, as detailed in this work on Future-Aware Quantization, necessitates a rigorous approach to algorithmic correctness. The study addresses the critical issue of error accumulation during post-training quantization, striving for a deterministic outcome even with reduced precision. This aligns with Marvin Minsky’s assertion: “The view that ‘anything is possible’ is a poison to thought.” The FAQ method, by proactively considering future activations, attempts to constrain the possibilities and ensure a predictable, reproducible result-a mathematically sound solution rather than a merely functional one. The method’s reliance on previewing activations embodies a commitment to establishing provable accuracy, a principle central to robust and reliable artificial intelligence systems.
What’s Next?
The introduction of Future-Aware Quantization (FAQ) represents a localized correction to a fundamentally imperfect process. While FAQ demonstrably mitigates error accumulation inherent in post-training quantization, it does not address the underlying asymmetry: the compression of information is, by definition, a lossy operation. The asymptotic behavior of error propagation, even with future activation awareness, remains an open question; will increasingly deep networks inevitably succumb to amplified quantization bias, requiring ever more sophisticated predictive mechanisms? The current work offers a temporary reprieve, not a lasting solution.
A more fruitful avenue of inquiry lies in exploring the theoretical limits of low-bit quantization. The observed performance gains with FAQ suggest that activations possess a hidden redundancy, an over-representation of information. Determining the minimal bit-width required to preserve essential semantic content – establishing a lower bound on representational entropy – would yield a more principled approach than empirical optimization. Such a constraint, expressed as an invariant, would provide a robust metric for evaluating quantization algorithms, superseding ad-hoc comparisons.
Finally, the reliance on future activations introduces a computational overhead. While acceptable for offline quantization, the latency incurred during inference remains a practical limitation. A truly elegant solution would reconcile predictive accuracy with computational efficiency, perhaps through the development of quantized approximations to the activation preview mechanism itself. The pursuit of minimal representation, constrained by provable error bounds, is the logical endpoint.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2602.02538.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Poppy Playtime Chapter 5: Engineering Workshop Locker Keypad Code Guide
- God Of War: Sons Of Sparta – Interactive Map
- Jujutsu Kaisen Modulo Chapter 23 Preview: Yuji And Maru End Cursed Spirits
- Poppy Playtime 5: Battery Locations & Locker Code for Huggy Escape Room
- Who Is the Information Broker in The Sims 4?
- Poppy Playtime Chapter 5: Emoji Keypad Code in Conditioning
- Someone Made a SNES-Like Version of Super Mario Bros. Wonder, and You Can Play it for Free
- Why Aave is Making Waves with $1B in Tokenized Assets – You Won’t Believe This!
- Pressure Hand Locker Code in Poppy Playtime: Chapter 5
- One Piece Chapter 1175 Preview, Release Date, And What To Expect
2026-02-05 02:16