Mapping the Quark Landscape at Extreme Densities
![The distribution of spins within a three-state Potts model, subjected to coarse-graining via the diffusion equation with [latex]D_t/a^2 = 0.5[/latex], demonstrates a clear phase transition: at [latex]\beta = 0.30[/latex] the system remains symmetric, while at [latex]\beta = 0.40[/latex] it enters a broken phase, indicating the sensitivity of spin configurations to subtle changes in system parameters.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.15720v1/figs/diffusion50b040l32.png)
New research utilizes a simplified model to chart the complex phase transitions of quark matter under conditions found in neutron stars and heavy ion collisions.
![The distribution of spins within a three-state Potts model, subjected to coarse-graining via the diffusion equation with [latex]D_t/a^2 = 0.5[/latex], demonstrates a clear phase transition: at [latex]\beta = 0.30[/latex] the system remains symmetric, while at [latex]\beta = 0.40[/latex] it enters a broken phase, indicating the sensitivity of spin configurations to subtle changes in system parameters.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.15720v1/figs/diffusion50b040l32.png)
New research utilizes a simplified model to chart the complex phase transitions of quark matter under conditions found in neutron stars and heavy ion collisions.
)))))[/latex] as a valid sequence.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.15714v1/imgs/chatgpt.png)
New research reveals that even the most advanced language models struggle with fundamental tasks, highlighting a critical need for more robust evaluation metrics.
![The system explores domain-wall profiles within a [latex]Z(3)[/latex] symmetry, demonstrating how chiral backreaction influences their structure and evolution as a natural consequence of the system’s inherent decay.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.15342v1/Fig4_PRL_pretty.png)
A new theoretical model details how the interplay of confinement and chiral symmetry breaking shapes phase transitions within a hidden sector governed by dark QCD.
A new framework leverages the power of locally-run artificial intelligence to identify security vulnerabilities hidden within Python code’s looping structures.
New analysis of hyperon-antihyperon pairs provides stringent tests of quantum mechanics against hidden-variable theories.
A new analysis reveals that current methods for identifying AI-written content are fundamentally flawed and easily bypassed.
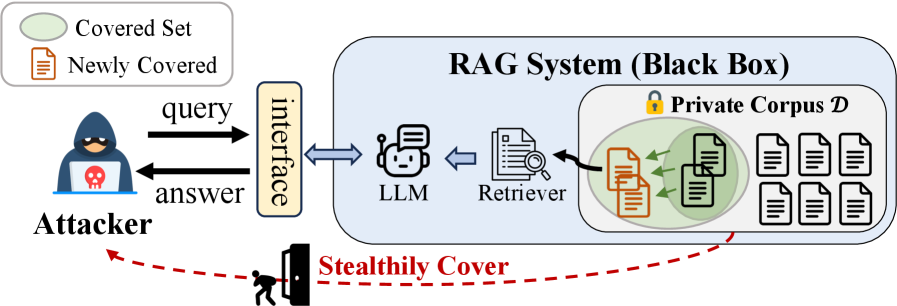
A new study reveals a potent attack framework capable of extracting sensitive data from Retrieval-Augmented Generation systems by intelligently navigating their underlying knowledge sources.
![The study reveals that subtle deviations from a simplified [latex]\hat{H}_{PXQ}[/latex] Hamiltonian-attributable to longer-range interactions-manifest as measurable changes in the average classical number of excitations, leakage from the single dimer subspace, and the averaged Rydberg population difference, despite nearly identical dynamics predicted by both the simplified and full [latex]\hat{H}_{0}[/latex] Hamiltonians across a system of length ten.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.15866v1/fig/Fig6_Ncl_single_excited_v1.png)
New research reveals how strongly interacting chains of Rydberg atoms can exhibit surprisingly predictable dynamics under certain conditions.
New optimizations to ciphertext multiplication are unlocking faster and more practical computations within the realm of homomorphic encryption.
As large language models become increasingly powerful, ensuring they can ‘unlearn’ incorrect information is critical, but existing techniques falter when applied to compressed AI models.