Future-Proofing Encryption: A Hybrid Approach to Quantum Security
A new implementation combines post-quantum cryptography with established symmetric encryption to deliver secure communication in the age of quantum computing.
A new implementation combines post-quantum cryptography with established symmetric encryption to deliver secure communication in the age of quantum computing.
![Distinct schedules for measuring the [latex]ZZZZZZZZ[/latex] syndrome within a quantum circuit exhibit differing logical error rates, as demonstrated by the timing of Pauli checks between data and ancilla qubits across surface code patches.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.12509v1/x1.png)
A new framework uses Monte Carlo Tree Search to dramatically improve the efficiency of syndrome measurement circuits, a critical step in protecting quantum information.
New research characterizes the quantum complexity class QMA through interactive quantum proofs, offering insights into the limits of efficient computation.
A new framework leverages code-based cryptography to enable secure aggregation of data, even in the face of quantum computing threats.
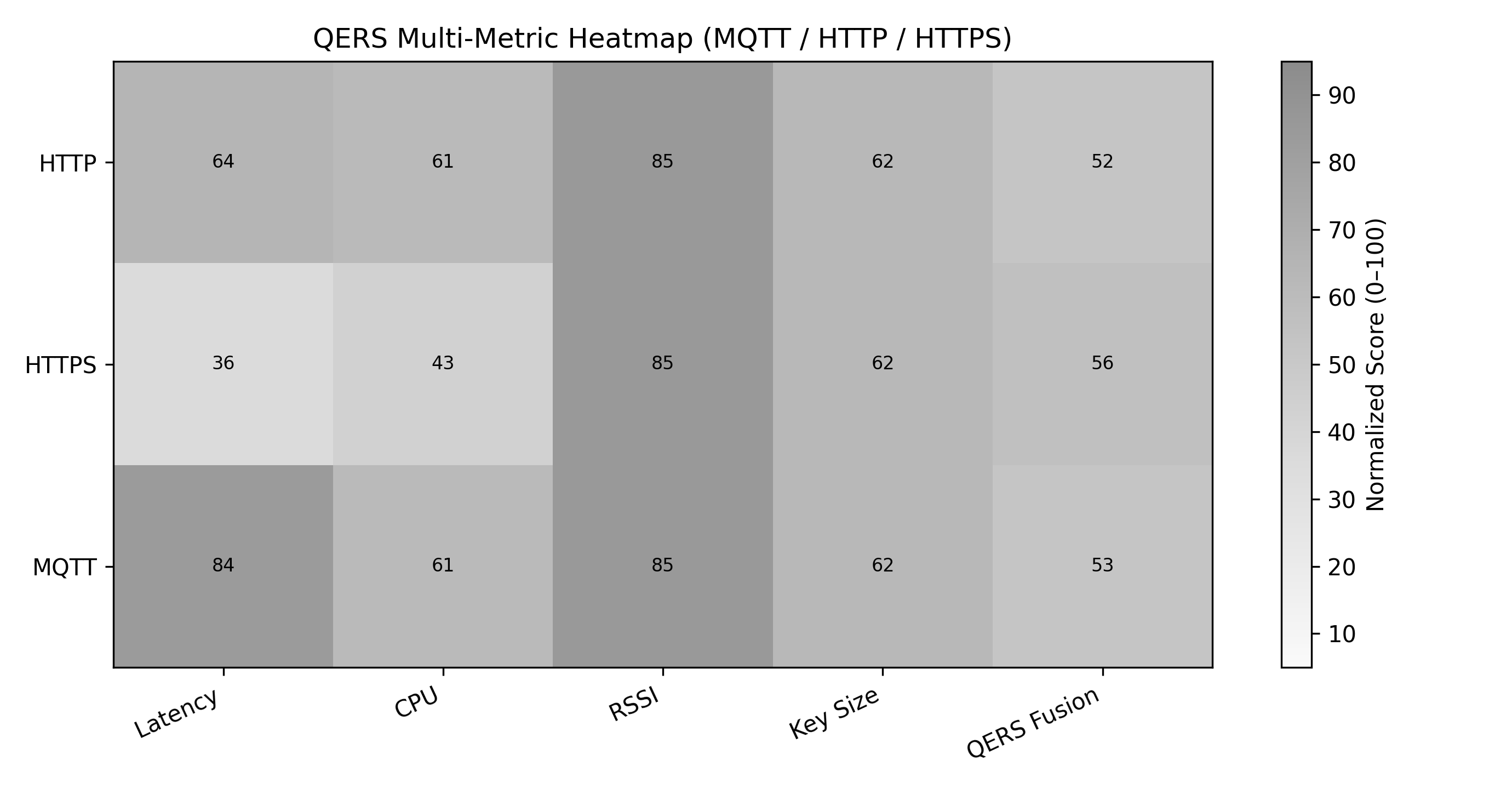
A new framework assesses the resilience of common communication protocols – MQTT, HTTP, and HTTPS – against the looming threat of quantum computing.
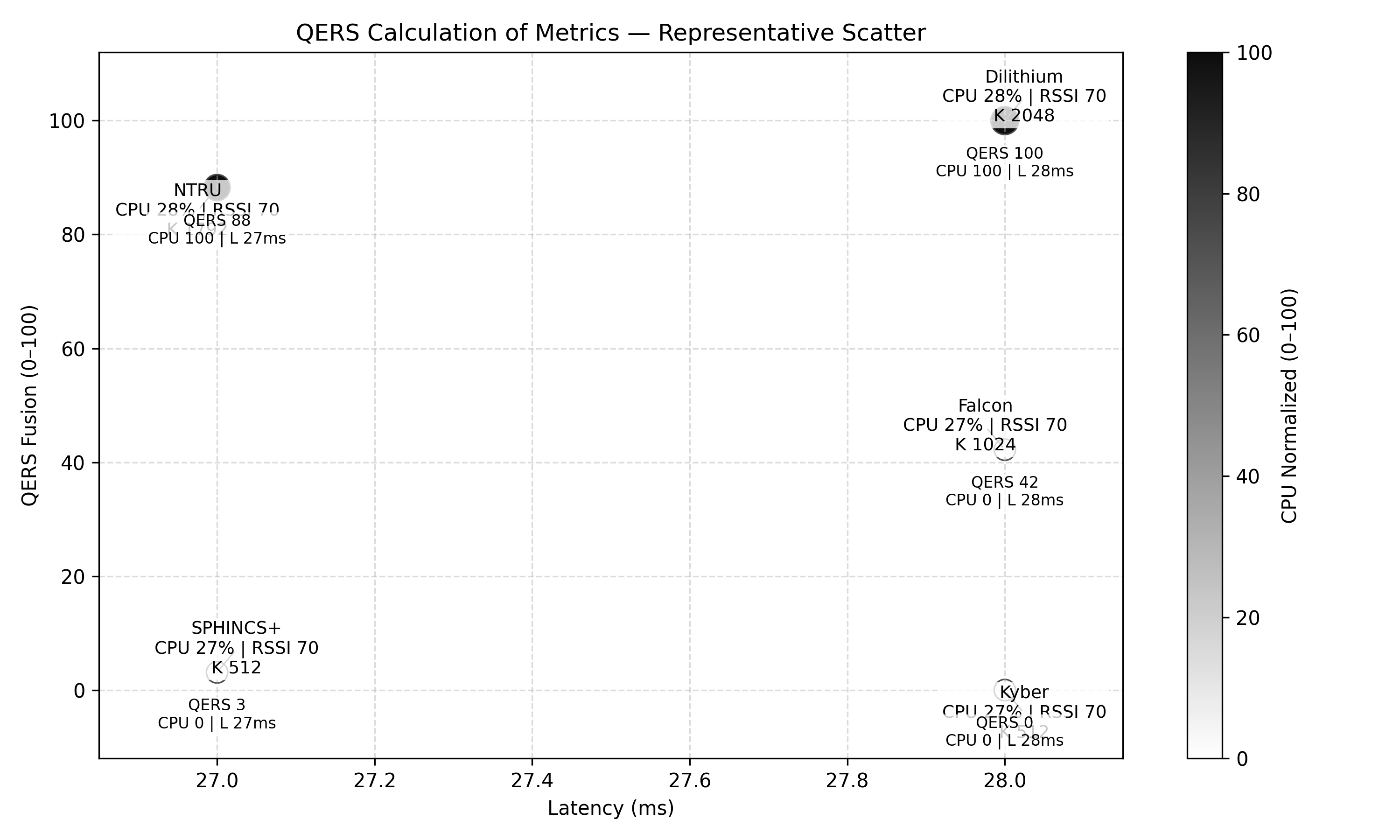
A new framework assesses the real-world resilience of post-quantum cryptography on constrained devices, moving beyond simple performance tests.
![The study establishes a 95% confidence level upper limit on the signal strength multiplier μ times the machine learning event yield [latex]S_{ev}[/latex] for the fully hadronic decay channel of [latex]Su \rightarrow u\chi \rightarrow u(Wb)[/latex], specifically when the mass of χ is 2 TeV and the parameter <i>D</i> equals 0.9.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.11181v1/x4.png)
A new study explores the potential to uncover ultraheavy diquarks decaying into multijet final states at the upcoming High-Luminosity Large Hadron Collider.
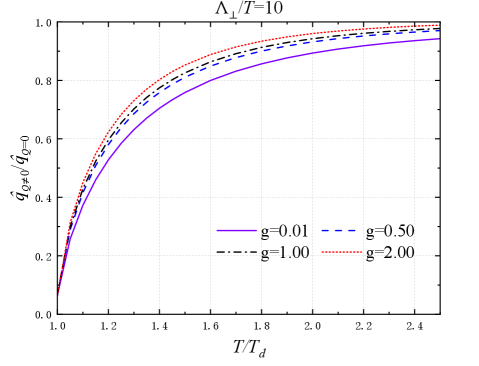
New research reveals a significant reduction in the energy loss experienced by fast-moving particles as they traverse the ultra-hot quark-gluon plasma created in heavy-ion collisions.
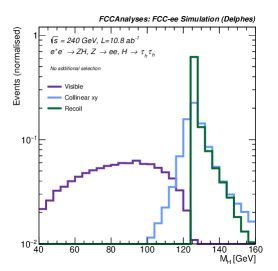
A new study details how a future circular collider could dramatically improve our understanding of the Higgs boson by precisely measuring its decay into tau leptons.
![Attention mechanisms are being refined to address the escalating costs of key-value (KV) caching-Multi-Head Attention’s independent projections ([latex]2LHd_h[/latex]) give way to compression in Multi-Latent Attention ([latex]Ld_c[/latex], where [latex]d_c \ll d[/latex]), then to shared projections in Multi-Query and Grouped-Query Attention, culminating in a novel Low-Rank KV approach that-by maintaining full-rank projections alongside low-rank residual updates ([latex]2L(d_h + Hr)[/latex])-achieves a balance between head diversity and caching efficiency comparable to Multi-Latent Attention.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.11471v1/figures/LowRankKVCache.png)
A new attention mechanism dramatically reduces the memory footprint of large language models without sacrificing performance.