Vitalik Buterin, the founder of Ethereum, has consistently explored methods to enhance the network’s decentralization. A new research by Toni Wahrstätter proposes modifications to Ethereum’s incentive structure for validators, aligning with Buterin’s vision.
The research explores the concept of “anti-correlation penalties” currently at play in Ethereum’s network. Large entities managing numerous validators can reduce costs, leading to dominance by a few major players. However, when multiple validators controlled by one entity fail simultaneously, it poses a risk for the entire network. To mitigate this risk, a novel approach suggests imposing penalties on validators that frequently fail together. This penalty system would incentivize a more diverse and independent pool of validators.
Essentially, if an abnormal number of validators fail to verify transactions (attestations) on Ethereum, they may incur a penalty. This mechanism ensures Ethereum‘s decentralization, reducing the likelihood that a single dominant validator holds excessive control.
Wahrstätter’s examination considers data spanning approximately 40 days, featuring roughly 9.3 billion legitimate validator actions. To explore potential impacts, the study contemplates implementing Vitalik’s suggested formula on this dataset.
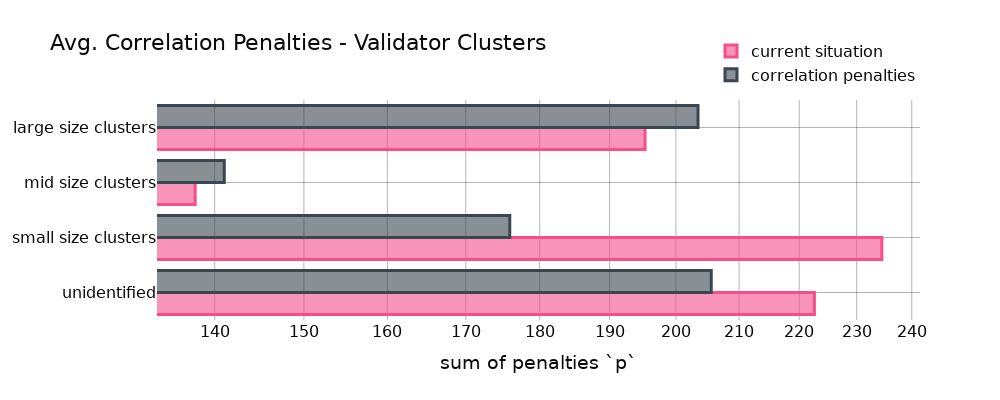
Staking operators, or those managing validators, will experience differing consequences based on their scale under the new system. Larger operators may face increased penalties, while smaller ones could profit. This aligns with the goal of deterring large-scale centralization through these penalties. It’s intriguing that an unidentified group of validators, potentially solo stakers, emerged as well, reflecting the network’s diversity.
The research examined the various software programs employed by validators in its assessment. The rationale behind this was that validators using identical software could potentially incur more severe penalties if they all encounter issues together. The results indicated minor variations between different clients, implying a high degree of software reliability.
Read More
- BTC PREDICTION. BTC cryptocurrency
- USD PHP PREDICTION
- LUNC PREDICTION. LUNC cryptocurrency
- USD COP PREDICTION
- LIT PREDICTION. LIT cryptocurrency
- BCH PREDICTION. BCH cryptocurrency
- ORAI PREDICTION. ORAI cryptocurrency
- USD CNY PREDICTION
- AVAX PREDICTION. AVAX cryptocurrency
- USD MYR PREDICTION
2024-04-09 14:37