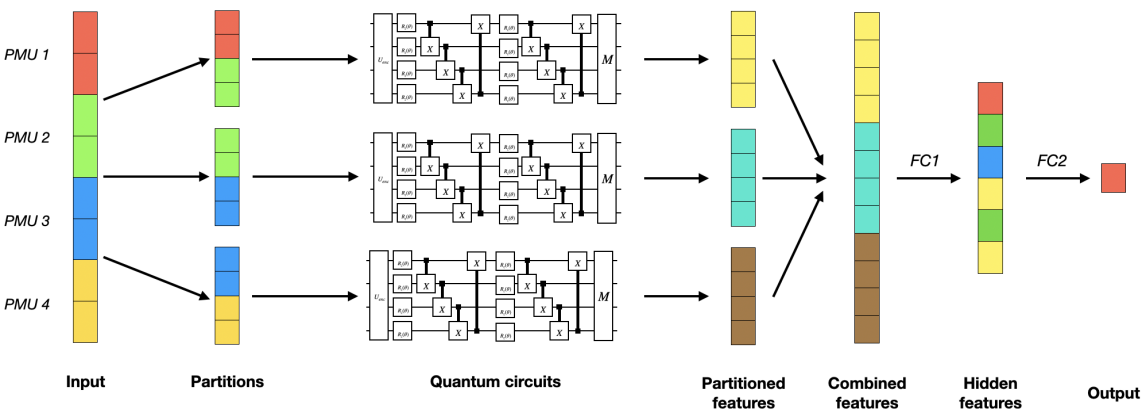
Predicting Solid-State Stability: A Benchmark for Advanced Density Functionals
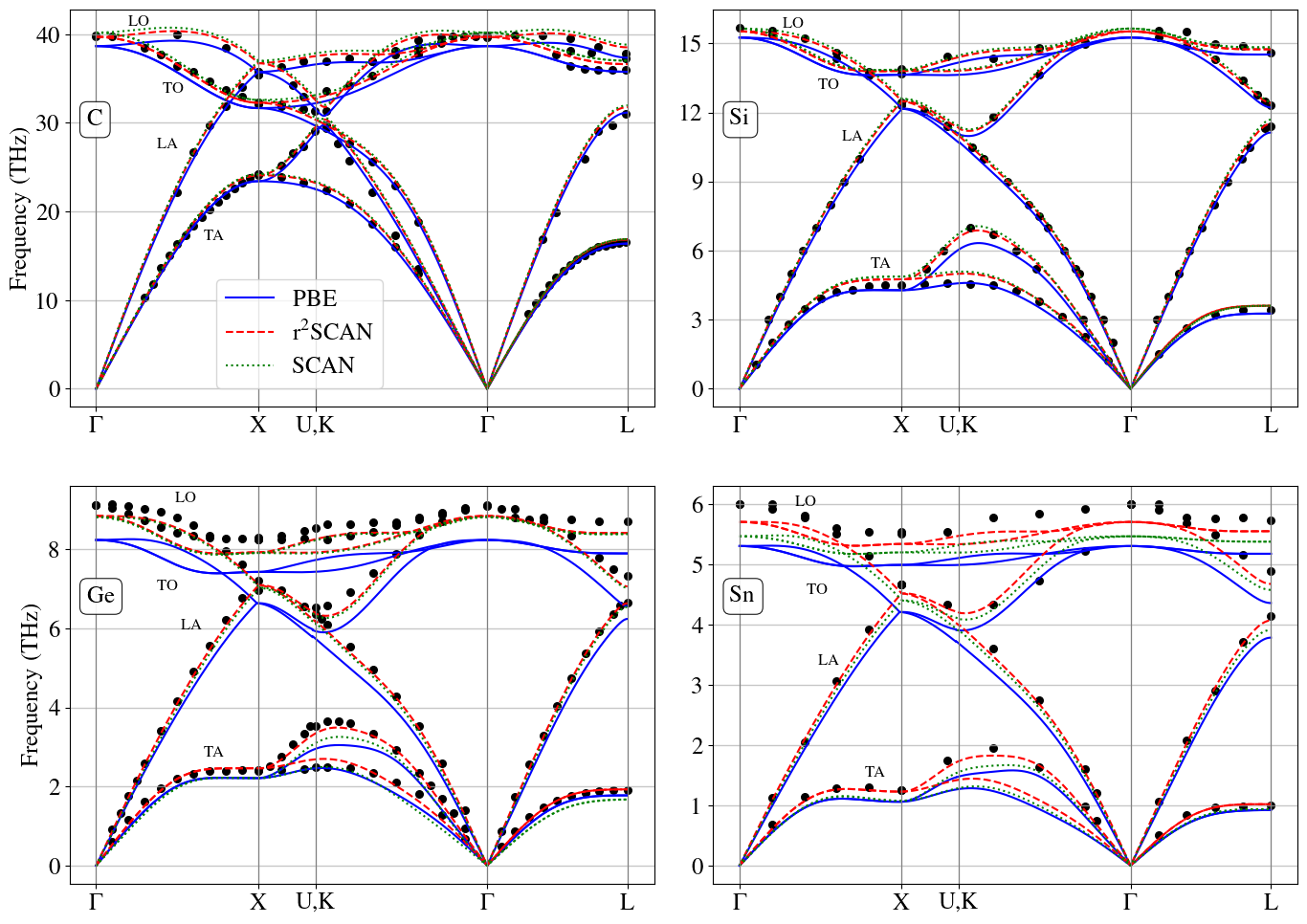
A new study rigorously tests the accuracy of modern density functional theory methods in predicting the structural behavior of group IV elements like silicon and germanium.
![Performance metrics demonstrate the capabilities of [latex]\mathsf{POD}[/latex] when operating with the eBCH(16,7)(16,7) coding scheme, indicating its efficacy within that specific communication architecture.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.11373v1/fig/eBCH_4_2_POD.png)
![The proposed LoRA oracle efficiently adapts large language models by learning low-rank approximations, enabling parameter-efficient transfer learning without extensive retraining of the original model weights [latex] \Delta w = BA [/latex], where [latex] B [/latex] and [latex] A [/latex] represent the low-rank matrices and [latex] w [/latex] denotes the original weights.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.11207v1/x1.png)